Why Are the Leaves of My Philodendron Splendid Turning Yellow?
Yellowing leaves on a Philodendron Splendid may result from various factors. Overwatering can lead to root oxygen deprivation, chlorosis, and root rot.
Conversely, underwatering causes water stress and stomatal closure. Poor drainage exacerbates waterlogging and impairs nutrient uptake.
Insufficient light affects photosynthesis, and temperature stress can damage cellular structures. Nutrient deficiencies disrupt metabolic processes, and pests or fungal infections impair vascular function.
Natural leaf senescence might also be a cause. Understanding these elements can guide corrective measures.
If you seek more detailed insights into each cause and its solutions, further information can be explored.
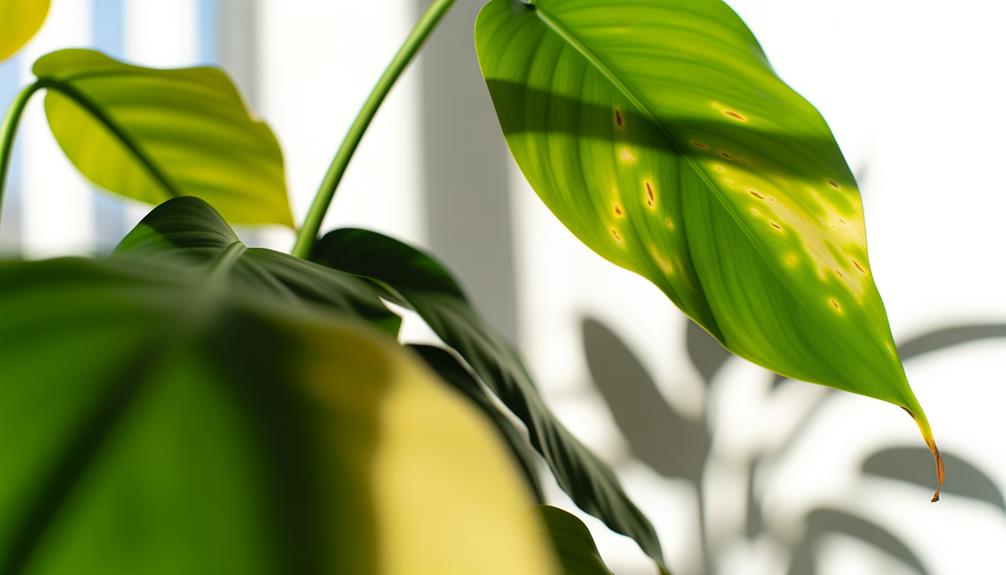

Key Takeaways
- Overwatering can lead to root oxygen deprivation, causing chlorosis and yellow leaves.
- Insufficient light reduces photosynthetic efficiency, resulting in yellowing leaves.
- Nutrient deficiencies, particularly nitrogen, can cause leaves to turn yellow.
- Pests and fungal infections can impair plant health, leading to yellow leaves.
- Natural aging of leaves can cause them to turn yellow as part of the senescence process.
Overwatering Issues
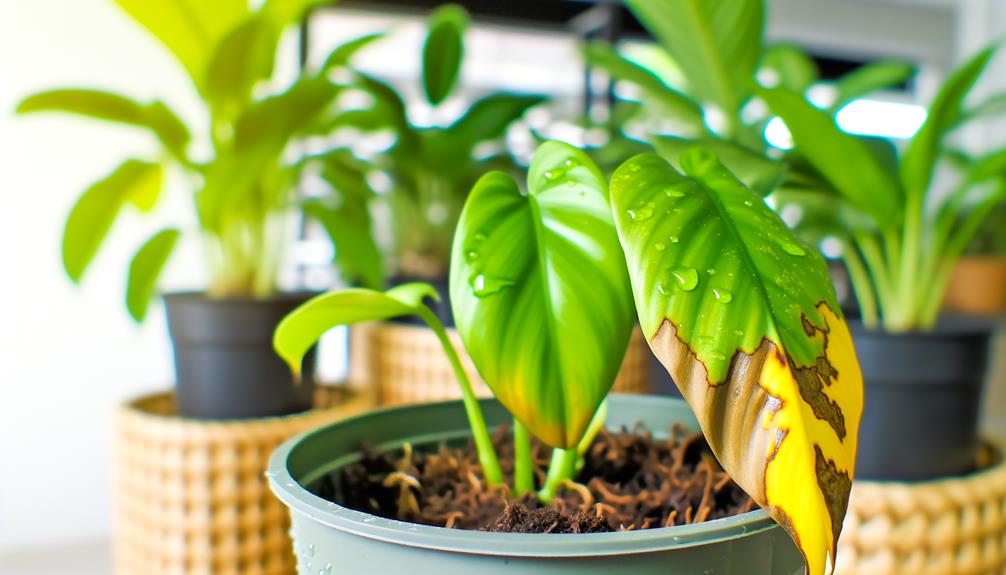

One of the primary causes of yellow leaves on Philodendron Splendid is overwatering, which leads to root oxygen deprivation and subsequent chlorosis.
Overwatering saturates the soil, creating anaerobic conditions that inhibit root respiration. This hypoxic environment disrupts the roots' ability to uptake essential nutrients, particularly iron, leading to chlorosis—characterized by yellowing of leaf tissue due to insufficient chlorophyll production.
Additionally, waterlogged soil can promote pathogenic fungal growth, exacerbating root rot. This pathological state further impairs water and nutrient transport within the plant, culminating in systemic stress and foliar discoloration.
Effective irrigation management, such as allowing soil to dry between waterings, is essential for maintaining the best root health and preventing the physiological cascade leading to yellow leaves.
Underwatering Effects
Inadequate watering leads to water stress in Philodendron Splendid, causing stomatal closure and reduced photosynthetic efficiency, which ultimately results in yellowing leaves. Water stress triggers abscisic acid (ABA) production, signaling stomatal guard cells to close and conserve water.
This closure inhibits carbon dioxide uptake, impairing the Calvin cycle and reducing chlorophyll synthesis. Consequently, chlorosis manifests as yellowing.
Prolonged dehydration further depletes turgor pressure, compromising cellular structure and metabolic activities. Insufficient water also hinders nutrient translocation via the xylem, exacerbating nutrient deficiencies.
The limited availability of essential elements like nitrogen and magnesium directly impacts chloroplast function, intensifying leaf discoloration. Maintaining an appropriate soil moisture level is crucial for the physiological well-being of Philodendron Splendid, ensuring vibrant, green foliage.
Poor Drainage
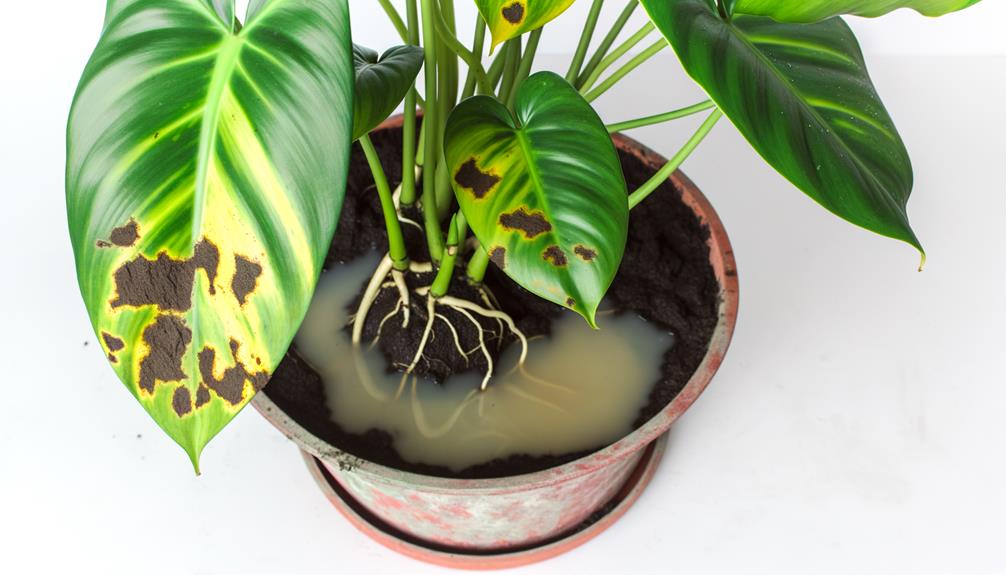

Poor drainage in the soil can lead to waterlogged conditions, which impede oxygen availability to the roots and promote anaerobic microbial activity, potentially causing root rot. This pathological condition compromises the plant's ability to uptake essential nutrients, manifesting as yellowing leaves.
Implementing effective container drainage solutions, such as the use of porous substrates and well-designed drainage holes, is critical to mitigating these risks.
Waterlogged Soil Issues
Excessive soil moisture due to insufficient drainage can lead to root rot, causing the philodendron splendid's leaves to turn yellow as a stress response. This condition arises when water accumulates around the root zone, resulting in hypoxic conditions that impair root function. Inadequate aeration and prolonged water saturation disrupt the plant's ability to absorb essential nutrients, including nitrogen and potassium, which manifests as chlorosis in the leaves.
Furthermore, waterlogged soil fosters anaerobic microorganisms, exacerbating the issue by producing phytotoxic compounds. To mitigate these problems, ensure the potting medium has ideal porosity and consider implementing a well-designed drainage system. Regularly monitor soil moisture levels and adjust watering practices to maintain a balanced moisture environment conducive to healthy root activity.
Root Rot Risk
Root rot, a prevalent issue in philodendron splendid cultivation, arises primarily from inadequate drainage that leads to prolonged soil saturation and anaerobic conditions. This excessive moisture environment fosters the proliferation of pathogenic fungi such as Pythium, Phytophthora, and Rhizoctonia, which degrade root tissue, impeding the plant's ability to absorb water and nutrients efficiently.
Consequently, the compromised root system triggers chlorosis, manifesting as yellowing leaves. The anaerobic conditions also facilitate hypoxic stress, further exacerbating root decay. Early detection of root rot is critical; symptoms include blackened, mushy roots and a foul odor emanating from the soil.
Addressing poor drainage promptly is essential to mitigate root rot risk and support the health and well-being of philodendron splendid.
Container Drainage Solutions
To effectively prevent waterlogging and subsequent root rot in philodendron splendid, implementing proper container drainage solutions is crucial. Utilize pots with multiple drainage holes to facilitate rapid water egress, minimizing soil water retention.
Incorporate a well-aerated potting medium composed of equal parts peat moss, perlite, and orchid bark to enhance porosity and drainage efficiency. Ensure drainage holes are unobstructed by employing mesh or coarse gravel at the base, which prevents soil compaction and promotes water movement.
Regular monitoring of substrate moisture levels using a soil moisture meter can preempt overwatering. Additionally, elevate containers on pot feet or saucers to avert water accumulation at the base, thereby sustaining the best root aeration and preventing phytopathogenic infections.
Insufficient Light
Inadequate light profoundly impacts the photosynthetic efficiency of Philodendron Splendid, leading to chlorosis and subsequent yellowing of leaves. This species needs moderate to bright indirect light to maintain peak physiological function.
Strategically placing the plant near east or north-facing windows can guarantee sufficient light intensity without exposing it to damaging direct sunlight.
Light Intensity Requirements
Subpar light intensity is a crucial factor contributing to the yellowing of Philodendron Splendid leaves. This species requires moderate to bright, indirect light to perform efficient photosynthetic activities. Inadequate light hampers chlorophyll production, affecting photosynthesis and resulting in chlorosis, characterized by yellowing leaves.
Light energy is vital for the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, driving plant growth and health. When lacking sufficient light, the plant reallocates limited resources, leading to nutrient deficiencies manifesting as yellow foliage.
Monitoring the light intensity using a light meter and ensuring it falls within the ideal range for Philodendron Splendid is essential. This will maintain proper photosynthetic function and prevent the leaves from turning yellow due to light inadequacy.
Optimal Placement Tips
Securing ideal positioning for Philodendron Splendid involves placing the plant in an area where it receives steady, moderate to bright indirect light to reduce the risk of yellowing leaves due to insufficient light exposure.
Inadequate light hinders the photosynthetic process, resulting in chlorosis, a condition marked by yellowing leaves. For optimal photosynthesis, position the Philodendron near east or west-facing windows, filtering direct sunlight with sheer curtains if necessary. Avoid north-facing windows, as they generally offer subpar light intensity.
Employing artificial grow lights can complement natural light, guaranteeing the plant gets the necessary photoperiod. Regularly rotating the plant ensures even light exposure, preventing stretching and encouraging robust growth.
Thoughtful consideration of light placement can notably improve the Philodendron's health and visual appeal.
Temperature Stress

Temperature stress in Philodendron splendid manifests primarily through the yellowing of leaves, which indicates cellular damage and disrupted physiological processes. This phenomenon is typically caused by exposure to subpar temperature ranges, either excessively high or low. Thermal extremes can impair photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and nutrient assimilation, leading to chlorosis.
Critical temperature thresholds for Philodendron splendid include:
- Best Temperature Range: 65°F to 78°F (18°C to 26°C)
- Cold Stress: Below 55°F (13°C), causing cellular rupture
- Heat Stress: Above 85°F (29°C), leading to protein denaturation
- Sudden Temperature Fluctuations: Rapid changes can shock the plant
- Extended Exposure: Chronic exposure to non-ideal temperatures
Maintaining stable, moderate temperatures is imperative for the health and vigor of Philodendron splendid, ensuring optimal physiological functionality and leaf coloration.
Nutrient Deficiencies
Nutrient deficiencies in Philodendron splendid often manifest as yellow leaves, resulting from inadequate levels of essential macro and micronutrients critical for chlorophyll production and overall plant health. Key nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and trace elements such as magnesium, iron, and manganese.
Nitrogen is pivotal for chlorophyll synthesis, and its deficiency leads to chlorosis, primarily in older leaves. Iron and magnesium deficiencies result in interveinal chlorosis, where leaf veins remain green while the surrounding tissue turns yellow. Phosphorus and potassium deficiencies, although less common, can also contribute to yellowing by impairing energy transfer and metabolic functions.
Ensuring balanced fertilization with a complete nutrient profile is fundamental to maintaining the vibrant green foliage characteristic of a healthy Philodendron splendid.
Pest Infestations
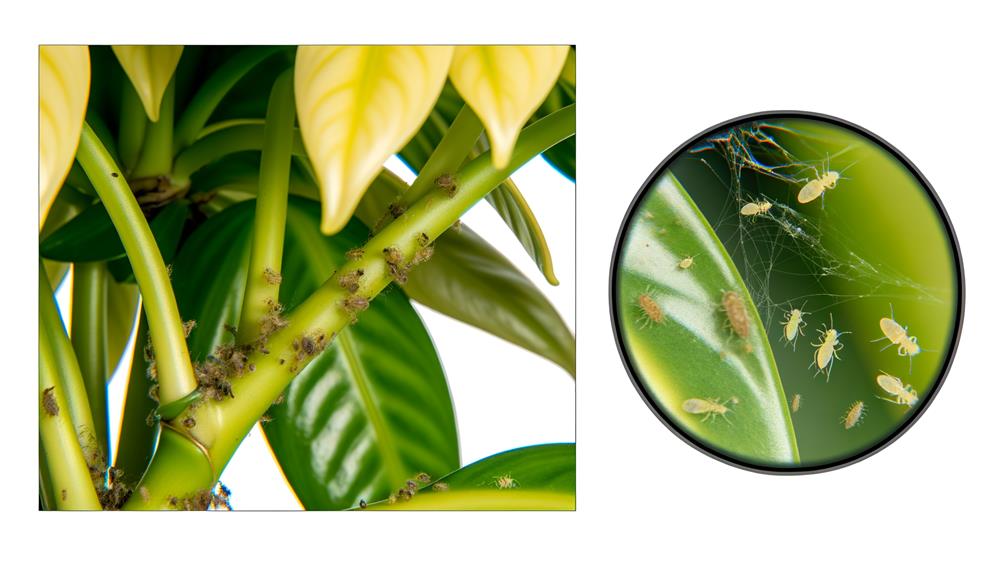

In addition to nutrient deficiencies, pest infestations are another significant factor contributing to yellow leaves on Philodendron splendid, with common culprits including spider mites, aphids, and mealybugs. These pests damage plant tissues by sucking sap, leading to chlorosis and compromised photosynthetic efficiency. Early detection and intervention are essential for managing pest infestations effectively.
Indicators of pest activity include:
- Visible pests: Small insects or webs on leaves and stems.
- Sticky residue: Honeydew excreted by aphids and mealybugs.
- Leaf distortion: Twisting or curling of foliage.
- Discolored spots: Localized yellowing or stippling.
- General decline: Wilting or reduced vigor.
Implementing integrated pest management strategies, such as biological control and appropriate chemical treatments, can mitigate these issues and restore plant health.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections, such as those caused by pathogens like *Phytophthora* or *Pythium*, can lead to significant yellowing of Philodendron splendid leaves due to impaired vascular function and subsequent nutrient transport disruption.
These fungi invade the plant's roots, causing root rot, which hinders the plant's ability to uptake water and essential nutrients. As a result, chlorosis manifests in the leaves, leading to a yellow appearance.
Additionally, these pathogens produce spores that propagate quickly in poorly-drained, overwatered soils, exacerbating the infection.
Effective management involves improving soil drainage, moderating watering practices, and applying fungicides specifically targeting these pathogens. Regular monitoring for early signs of infection is essential to mitigate the spread and maintain the plant's overall health.
Aging Leaves
Aging leaves on Philodendron splendid naturally turn yellow as part of the plant's senescence process, wherein older foliage is systematically degraded and resources are reallocated to newer growth. Senescence is a programmed physiological mechanism that optimizes resource utilization within the plant. During this phase, chlorophyll breakdown occurs, manifesting as yellow discoloration. This process is crucial for the plant's overall health and well-being.
Key indicators of natural leaf aging include:
- Position: Older leaves are typically located at the lower regions of the plant.
- Symmetry: Yellowing is uniform and symmetrical.
- Progression: Gradual change from green to yellow.
- Absence of Necrosis: No browning or blackening.
- Leaf Drop: Eventual detachment of the aged leaves.
Understanding this natural cycle helps in distinguishing it from pathological causes.
Conclusion
To sum up, the yellowing of Philodendron splendid leaves can be attributed to several factors, including overwatering, underwatering, poor drainage, insufficient light, temperature stress, nutrient deficiencies, pest infestations, fungal infections, and the natural aging process of leaves.
Each of these factors disrupts the physiological balance of the plant, underscoring the intricate interplay between environmental conditions and plant health.
Addressing these issues through precise horticultural practices is crucial for maintaining the health and aesthetic appeal of Philodendron splendid.






