What Is the Scientific Name of the Philodendron Little Hope?
The scientific name of the Philodendron Little Hope is *Philodendron bipinnatifidum* 'Little Hope'. This cultivar, known for its compact and dense growth habit, belongs to the Araceae family and showcases deeply lobed, emerald-green foliage.
It thrives in well-draining, organic-rich substrates and adapts well to various indoor environments. Understanding its precise scientific nomenclature is essential for accurate identification and proper horticultural practices.
Scientific names provide a universal language to avoid ambiguity, reflecting the plant's unique characteristics and phylogenetic relationships. To explore more about the Philodendron Little Hope's care requirements and distinguishing features, continue your inquiry here.

Key Takeaways
- The scientific name of Philodendron Little Hope is Philodendron bipinnatifidum.
- Philodendron bipinnatifidum belongs to the Araceae family.
- It is a compact cultivar of Philodendron bipinnatifidum.
- Scientific names eliminate confusion caused by common names.
- Philodendron bipinnatifidum features deeply lobed, emerald-green foliage.
Philodendron Little Hope Overview
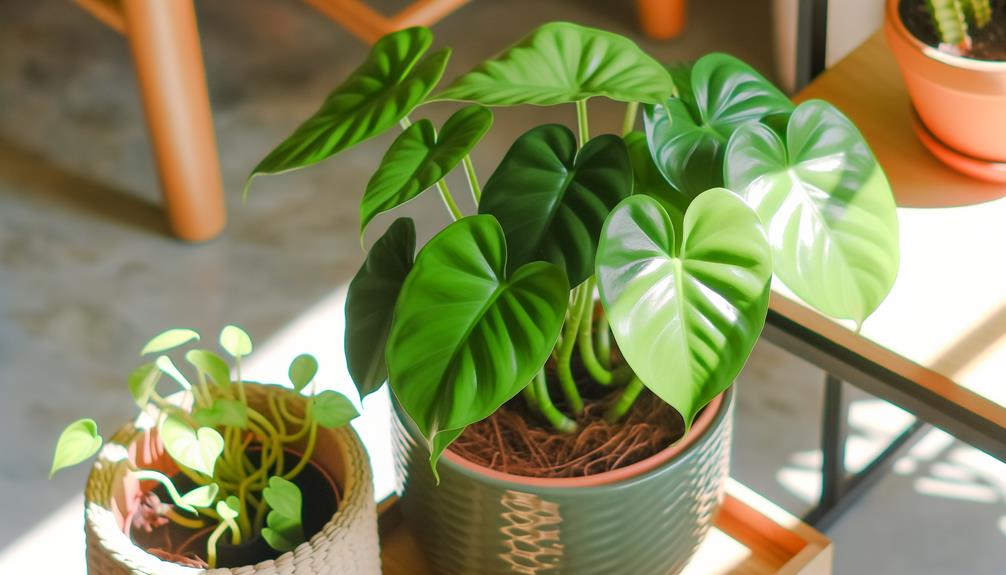

The Philodendron Little Hope is a compact and dense cultivar of the Philodendron bipinnatifidum species. It is renowned for its deeply lobed, emerald-green foliage and robust growth habit. This perennial evergreen features pinnately divided leaves and exhibits ideal ornamental value in both residential and commercial settings.
Its foliage is characterized by pronounced midribs and undulating margins, contributing to its aesthetic appeal and botanical interest. With a moderate growth rate, this cultivar achieves a manageable size, typically reaching heights of 2 to 3 feet and a similar spread.
The plant thrives in well-drained, organic-rich substrates and requires indirect light conditions to maintain its vibrant coloration. Additionally, its adaptability to various indoor environments underscores its popularity among horticultural enthusiasts and interior landscapers.
Importance of Scientific Names
Utilizing scientific names is essential for ensuring precise identification and classification of plants within the botanical community. These binomial nomenclatures, derived from Latin or Greek, provide a universal language that transcends regional and linguistic barriers.
The scientific name, typically composed of the genus and species, eliminates ambiguity that common names might introduce. For instance, Philodendron bipinnatifidum 'Little Hope' precisely identifies this specific cultivar, ensuring consistency across scientific literature and horticultural practices.
Additionally, scientific names reflect phylogenetic relationships, aiding in understanding evolutionary links and ecological niches. This systematic approach facilitates communication, research, and conservation efforts, ensuring that taxa are correctly identified, studied, and preserved across diverse biogeographical regions.
Classification Hierarchy

The classification hierarchy of the Philodendron Little Hope spans several taxonomic rank categories.
Beginning with its placement in the Plantae kingdom, it extends through various levels including order, family, genus, and species.
Belonging to the Araceae family, this plant is characterized by its unique morphological and physiological traits that distinguish it from other members of the plant kingdom.
Detailed examination of its taxonomic classification provides a structured framework for understanding its botanical relationships and evolutionary lineage.
Taxonomic Rank Categories
Within the classification hierarchy, Philodendron Little Hope is categorized under the family Araceae. Understanding its taxonomic rank involves recognizing its position in a structured system of classification.
The primary ranks include Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. Philodendron Little Hope belongs to the Kingdom Plantae, indicating it is a plant. It falls under the Phylum Magnoliophyta, signifying it is a flowering plant.
Within the Class Liliopsida, it is classified among monocotyledons. The Genus Philodendron places it among a diverse group of tropical plants. Each taxonomic rank provides a more specific identification, culminating in its designation as a distinct species within the broader Araceae family, thereby reflecting its unique botanical characteristics and evolutionary relationships.
Plant Family Details
In the classification hierarchy, the family Araceae encompasses a diverse array of species, including the Philodendron Little Hope, characterized by their unique inflorescences and often intricate leaf structures.
Araceae, commonly known as the Arum family, is distinguished by its spadix and spathe floral arrangement. Members of this family exhibit a wide range of morphological diversity, from terrestrial to epiphytic growth forms.
The genus Philodendron, within this family, is notable for its climbing and non-climbing species that thrive in tropical environments. Philodendrons are adapted to low-light conditions, making them popular as ornamental houseplants.
The intricate venation patterns and lobed leaves of Philodendron Little Hope underscore the evolutionary adaptability and aesthetic appeal inherent to the Araceae family.
Family and Genus
Belonging to the Araceae family, the Philodendron Little Hope is classified under the genus Philodendron, known for its diverse and extensive range of species. The Araceae family encompasses a wide array of monocotyledonous flowering plants, often referred to as the arum family. The genus Philodendron, characterized by its versatile morphological traits, includes climbing, creeping, and non-climbing species. The following table illustrates key characteristics of the Araceae family and the Philodendron genus:
| Characteristic | Araceae Family | Philodendron Genus |
|---|---|---|
| Flower Type | Spadix with spathe | Inflorescence structure |
| Leaf Arrangement | Alternate or spiral | Simple leaves |
| Habitat | Tropical, subtropical | Rainforests, wetlands |
| Growth Form | Herbaceous, climbing | Epiphytic, terrestrial |
| Reproductive | Monoecious, bisexual | Monoecious |
This classification underscores the Philodendron's adaptability and ecological diversity.
Species Identification
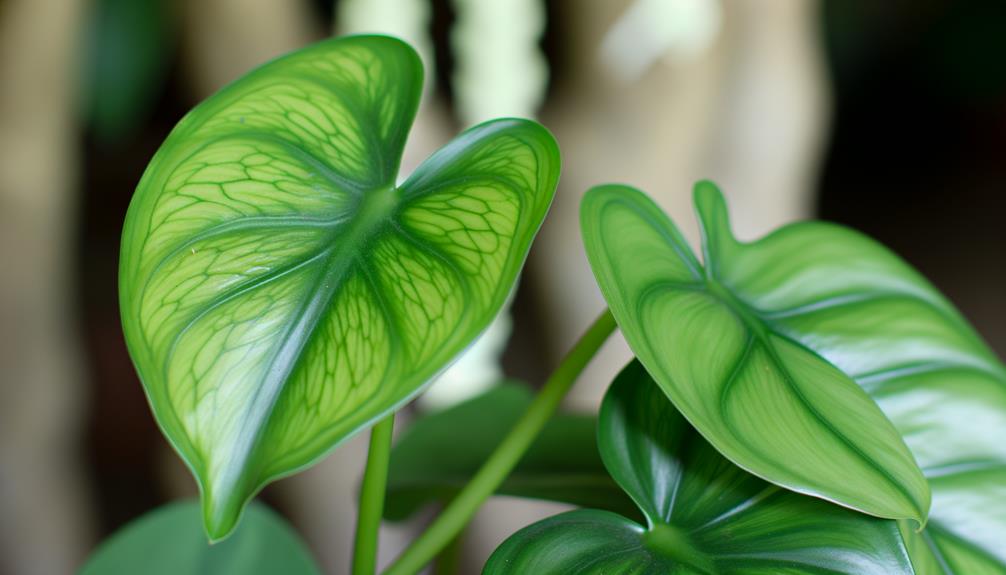

Species identification of the Philodendron Little Hope necessitates detailed examination of its morphological traits. Particularly, its compact growth habit, deeply lobed leaves, and distinct venation patterns. The plant exhibits a bushy growth form, rarely exceeding 2 feet in height, which distinguishes it from other Philodendron species.
Its leaves are characterized by deep lobes that extend towards the central vein, creating a finger-like appearance. The venation is prominent, with a primary midrib from which secondary veins radiate, forming a reticulate pattern. The petioles are relatively short and sturdy, supporting the leaf blade efficiently.
These morphological characteristics are critical for accurate species identification, aiding botanists and horticulturists in distinguishing Philodendron Little Hope from similar cultivars.
Botanical Nomenclature
The botanical nomenclature of the Philodendron Little Hope adheres strictly to the binomial system, ensuring accurate classification and universal communication among scientists and horticulturists.
This system, formalized by Carl Linnaeus, employs Latin or Latinized names to uniquely identify species. In this instance, the Philodendron Little Hope is classified under the genus Philodendron, which encompasses a variety of tropical plants known for their diverse morphology and adaptive growth forms.
The specific epithet, coupled with the genus name, provides a precise identifier for the species. This standardized naming mechanism facilitates consistent reference across different regions and languages, thereby supporting botanical research, conservation efforts, and horticultural practices.
Accurate nomenclature is pivotal in maintaining scientific rigor and enhancing collaboration.
Origin of the Name
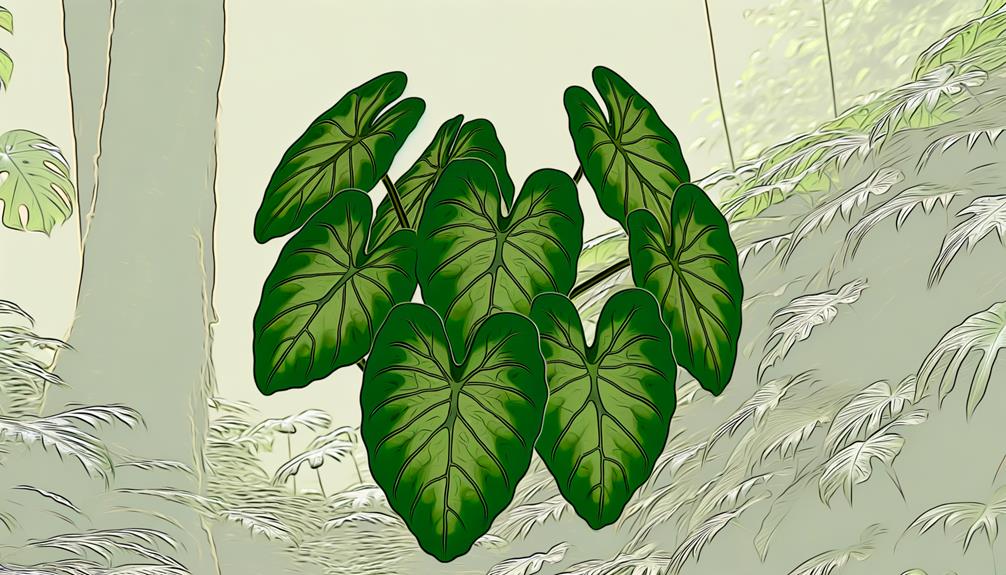
The etymology of 'Philodendron' is rooted in Greek, combining 'philo,' signifying love or affection, and 'dendron,' representing tree, reflecting the plant's climbing nature.
Botanical naming conventions, governed by the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), maintain standardized classification.
Over time, the evolution of plant names has mirrored advancements in botanical science and phylogenetic understanding, solidifying the significance of accurate nomenclature.
Philodendron's Greek Roots
Derived from the Greek words 'philo,' meaning love or affection, and 'dendron,' meaning tree, the name Philodendron aptly reflects the plant's climbing and tree-loving nature. This etymological origin underscores its biological inclination to thrive in arboreal environments, showcasing its adaptability and affinity for tree habitats.
The genus Philodendron comprises numerous species, each exhibiting unique morphological characteristics.
- Philo: Signifies affection or affinity, illustrating the plant's symbiotic relationship with trees.
- Dendron: Denotes tree, indicative of the plant's ecological niche and growth habits.
- Adaptability: Reflects the species' ability to thrive in diverse environmental conditions, often as epiphytes on trees.
Understanding these roots enhances appreciation for the Philodendron's ecological role and adaptive strategies.
Botanical Naming Conventions
In botanical nomenclature, the Philodendron Little Hope follows strict conventions established by the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), guaranteeing a universal and systematic classification.
The ICN mandates the use of Latin or Latinized names to provide consistency and clarity in plant identification. The genus name 'Philodendron' is derived from Greek words 'philo,' meaning love, and 'dendron,' meaning tree, reflecting the plant's growth habit.
The specific epithet 'Little Hope' distinguishes this particular cultivar within the Philodendron genus. Adherence to ICN principles guarantees that each plant name is unique and universally recognized, facilitating accurate communication among botanists, horticulturists, and researchers worldwide.
This systematic approach underpins the scientific study and conservation of plant species.
Evolution of Plant Names
Understanding the evolution of plant names involves tracing the linguistic and cultural influences that have shaped botanical nomenclature over centuries. The taxonomic classification of plants, such as the Philodendron Little Hope, reflects a structured system that incorporates Latin and Greek roots, regional vernaculars, and historical contexts.
- Linguistic Roots: Many scientific names derive from Latin or Greek, providing a universal language for taxonomy.
- Cultural Influences: Local names and indigenous knowledge often contribute to the nomenclature, reflecting the plant's geographical and cultural heritage.
- Historical Context: Botanical names can also honor individuals who contributed significantly to botany, such as explorers or scientists.
This intricate evolution ensures that each plant's name encapsulates its identity, origin, and historical significance.
Characteristics of Little Hope
Philodendron Little Hope displays deeply lobed, glossy green leaves that show a compact and dense growth habit, making it an ideal choice for interior landscaping.
The foliage is characterized by its pinnately lobed structure, which contributes to an aesthetically pleasing, lush appearance. Leaves typically measure between 15-25 cm in length, displaying a vibrant hue that persists year-round.
The plant's growth form is clumping, with multiple stems arising from a central root system, promoting a bushy and robust profile.
Adaptability to low-light conditions and moderate humidity levels further enhances its suitability for indoor environments. Additionally, Philodendron Little Hope demonstrates moderate drought tolerance, requiring well-draining soil and infrequent watering to thrive, ensuring minimal maintenance demands for caretakers.
Differences From Other Philodendrons

Frequently distinguished by its compact size and deeply lobed, glossy green leaves, the Little Hope variety showcases unique morphological traits that differentiate it from other Philodendrons.
Unlike the vining species, Little Hope maintains a bushy, clump-forming growth habit, making it well-suited for confined spaces. Its leaves are noticeably smaller yet denser compared to larger-leaved cousins like Philodendron bipinnatifidum.
Key differences include:
- Growth Habit: Little Hope forms compact clumps, whereas many Philodendrons exhibit vining or sprawling growth.
- Leaf Morphology: Smaller, deeply lobed leaves with a consistent glossy texture distinguish it from broader, less lobed leaves of other species.
- Size: Overall, a more diminutive stature, ideal for tabletop or small area placements, as opposed to the larger, floor-dominating species.
Cultivation and Care
Cultivation of the Philodendron Little Hope requires specific environmental parameters, including moderate indirect light and well-draining potting mix to achieve ideal growth.
Proper irrigation practices, characterized by maintaining consistently moist soil without waterlogging, are crucial to prevent root rot.
Additionally, periodic fertilization with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer enhances vigorous foliar development and overall plant health.
Ideal Growing Conditions
To achieve best growth and health, the Philodendron Little Hope requires a balance of well-drained soil, moderate moisture, and indirect sunlight. This tropical plant thrives in a porous, organic-rich potting mix that ensures proper aeration and drainage.
The ideal moisture range is between 40% and 60%, which can be maintained using a humidifier or by placing the plant on a pebble tray with water.
Bright, indirect sunlight is essential; direct sunlight can scorch its leaves, while low light may inhibit growth.
- Soil: Use a mix containing peat, perlite, and pine bark for optimal aeration and drainage.
- Humidity: Maintain 40%-60% moisture, supplementing with a humidifier if necessary.
- Light: Place in bright, indirect light, avoiding direct sun exposure.
Watering and Fertilization
Proper watering and fertilization are crucial for the Philodendron Little Hope to maintain its vibrant foliage and robust growth. This tropical plant thrives in consistently moist but well-drained soil. Over-watering can lead to root rot, so it is crucial to allow the top inch of soil to dry out between waterings.
Utilize a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer, diluted to half strength, every 4-6 weeks during the growing season to supply essential nutrients. Ensure the application is uniform to prevent nutrient imbalances. Additionally, reduce fertilization frequency in the dormant winter months to avoid excessive fertilization, which can cause leaf burn.
Monitoring and adjusting these practices will promote ideal health and longevity for the Philodendron Little Hope.
Common Misconceptions

Despite its popularity among houseplant enthusiasts, the Philodendron Little Hope is often mistakenly identified as a separate species rather than a cultivar of Philodendron bipinnatifidum. This misconception can lead to confusion in care requirements and botanical classification.
Several factors contribute to this misunderstanding:
- Nomenclatural Confusion: The common name 'Little Hope' suggests a distinct species, but it is, in fact, a compact variety of the larger P. bipinnatifidum.
- Morphological Similarities: While smaller in size, its leaf shape and growth habit closely resemble those of its parent species, making it challenging to differentiate.
- Marketing Misrepresentation: Retailers and nurseries often label these plants inaccurately, further perpetuating the myth of it being a separate species.
Understanding these nuances is essential for proper plant identification and care.
Benefits of Knowing the Scientific Name
Understanding the precise scientific classification of the Philodendron Little Hope as a cultivar of Philodendron bipinnatifidum offers several advantages, including more accurate guidelines for care, improved communication among botanists, and enhanced consistency in horticultural practices. This classification facilitates targeted research and accurate identification of plant characteristics. Scientific nomenclature also aids in standardizing terminology, thereby reducing ambiguities. Below is a table summarizing key benefits:
| Benefit | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Tailored Care Instructions | Customized care instructions based on species traits | Watering frequency, sunlight requirements |
| Consistent Communication | Uniform language among professionals | Accurate exchange of care techniques |
| Uniformity in Horticulture | Standard practices across regions | Standard pest control methods |
| Research Support | Focused scientific studies | Genetic research, growth pattern analysis |
| Clear Identification | Distinct differentiation from similar species | Avoiding misidentification in plant nurseries |
This structured approach ensures the best growth and health of the Philodendron Little Hope.
Conclusion
Understanding the scientific name of Philodendron 'Little Hope'—Philodendron bipinnatifidum—is critical for accurate identification, classification, and care.
Despite potential objections regarding the complexity of scientific terminology, these names provide a universal language that transcends common names, preventing misidentification.
This precision is vital for horticulturists and botanists who rely on specific characteristics to differentiate between similar species.
Knowing the scientific name guarantees proper cultivation practices, ultimately fostering healthier plant growth and contributing to broader scientific knowledge.






