What Is the Scientific Name of the Philodendron Cordatum?
The scientific name of the Philodendron Cordatum is Philodendron hederaceum var. oxycardium.
It is a perennial climbing plant characterized by heart-shaped, dark green, glossy leaves, and a vining growth habit. Native to the tropical rainforests of Brazil, this plant thrives in humid environments and often grows as an epiphyte on trees.
The classification process employed both morphological and genetic analyses to differentiate it from closely related species. Understanding the taxonomy and botanical characteristics of Philodendron Cordatum is essential for accurate identification and broader botanical study.
Further details about its unique features await exploration.

Key Takeaways
- The scientific name of Philodendron Cordatum is Philodendron cordatum.
- It follows the binomial naming system, which includes the genus and species.
- Philodendron cordatum is native to the tropical rainforests of Brazil.
- The species name "cordatum" refers to its heart-shaped leaves.
- It belongs to the Araceae family, known for its diverse tropical plants.
Overview of Philodendron Cordatum

Philodendron cordatum, commonly known as the Heartleaf Philodendron, is a perennial climbing plant characterized by its heart-shaped leaves and vining growth habit.
This plant belongs to the Araceae family and exhibits a robust climbing mechanism facilitated by aerial roots. The leaves are typically dark green, glossy, and can reach up to 30 centimeters in length under ideal conditions.
Its growth is vigorous, often requiring structural support for vertical expansion. Native to tropical regions, Philodendron cordatum thrives in humid environments with indirect light.
It is well-adapted to indoor cultivation, making it a popular choice among horticulturists and plant enthusiasts. Additionally, it exhibits significant resilience to varying environmental conditions, contributing to its widespread cultivation and use in ornamental horticulture.
Scientific Naming Process
The scientific naming process, also known as binomial nomenclature, involves a systematic approach to assigning universally accepted names to plant species, ensuring clarity and consistency in botanical classification. This methodology, established by Carl Linnaeus, employs two Latinized names: the genus and species. The genus, a broader category, groups related plants, while the species denotes a specific organism within that genus.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Genus | Broad category grouping related species |
| Species | Specific organism within a genus |
| Binomial | Two-part naming system (Genus species) |
| Latinized | Naming convention using Latin or Latin-like forms |
| Uniformity | Guarantees universal understanding and communication |
This structured framework provides a universal language for scientists worldwide, eliminating ambiguities and facilitating precise identification and study of plant species.
Taxonomy of Philodendron Cordatum
The taxonomy of Philodendron cordatum is located within the family Araceae, under the genus Philodendron, characterized by its heart-shaped leaves and climbing growth habit.
Classification within the genus involves thorough morphological and genetic analyses to guarantee precise species identification.
This process includes evaluating phenotypic traits and using molecular markers to differentiate Philodendron cordatum from closely related species.
Family and Genus Classification
Belonging to the family Araceae, Philodendron cordatum is classified within the genus Philodendron, which encompasses a diverse group of tropical plants.
The family Araceae, commonly known as aroids, is characterized by its flowering plants with a unique inflorescence structure known as a spadix, often accompanied by a spathe.
Within this family, the genus Philodendron is notable for its extensive variety, comprising over 450 species.
Philodendrons exhibit a range of growth habits, including climbing, epiphytic, and terrestrial forms, adapted to various tropical environments.
The genus is distinguished by its typically large, lobed leaves and aerial roots, features that enhance its adaptability and ecological success.
Philodendron cordatum, specifically, is appreciated for its heart-shaped foliage and resilient growth.
Species Identification Process
In the species identification process of Philodendron cordatum, taxonomists rely on a combination of morphological characteristics, genetic analysis, and ecological data to accurately classify and distinguish it from closely related species. This detailed process guarantees precise taxonomy and involves several key steps:
- Morphological Characteristics: Thorough examination of leaf shape, size, and venation patterns.
- Genetic Analysis: Sequencing specific DNA markers to validate phylogenetic relationships.
- Ecological Data: Investigating the plant's native habitat, growth conditions, and ecological interactions.
- Comparative Analysis: Cross-referencing with herbarium specimens and historical records.
- Expert Consultation: Collaborating with botanists specializing in the Araceae family.
This rigorous approach guarantees accurate species identification, essential for biodiversity conservation and botanical research.
Genus Philodendron
Characterized by a vast diversity of species, the genus Philodendron encompasses a wide range of tropical plants known for their distinctive foliage and adaptability to various environmental conditions. This genus belongs to the family Araceae and is comprised of approximately 489 species.
Philodendrons exhibit a variety of growth forms, including epiphytic, terrestrial, and hemiepiphytic habits. The leaves are typically large, often lobed or deeply incised, and can vary significantly in shape, size, and texture. The inflorescence is a spadix surrounded by a spathe, a common feature in Araceae.
Philodendrons are highly valued in horticulture for their aesthetic appeal and robustness, making them popular in both indoor and outdoor plant collections.
Species Cordatum

The species Cordatum, part of the genus Philodendron, is characterized by its heart-shaped leaves and vining growth habit. It is botanically classified under the family Araceae and is native to the tropical rainforests of Brazil.
Detailed studies of its native habitat reveal its preference for humid, shaded environments where it typically grows as an epiphyte on trees.
Botanical Classification Details
Belonging to the Araceae family, Philodendron cordatum is a perennial climbing plant distinguished by its heart-shaped leaves and vining growth habit. This species is classified under the genus Philodendron, known for its extensive diversity and adaptability.
The botanical classification details include:
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Order: Alismatales
- Family: Araceae
- Genus: Philodendron
- Species: P. cordatum
Philodendron cordatum exhibits distinct morphological features such as glossy, green, cordate leaves that facilitate efficient photosynthesis. The plant's climbing nature is supported by aerial roots, allowing it to anchor onto various surfaces.
It is essential for taxonomists and horticulturists to recognize these characteristics for accurate identification and classification within the broader Philodendron genus.
Native Habitat Information
Native to the tropical rainforests of Brazil, Philodendron cordatum thrives in humid, shaded environments where it clings to tree trunks and other vertical surfaces using its aerial roots.
This epiphytic species is adapted to the understory layer of the rainforest, where light is diffused through the dense canopy above. The microclimate of this habitat provides consistent moisture and high humidity, essential for the plant's growth and physiological functions.
Philodendron cordatum's leaves are designed to efficiently capture limited sunlight, and its roots facilitate nutrient absorption from organic debris accumulating on host trees.
This species' ability to adapt to varying light levels and moisture conditions makes it resilient in its native ecosystem, contributing to its widespread distribution within tropical regions.
Historical Background
Tracing its origins to the rich biodiversity of South American rainforests, Philodendron cordatum has a fascinating historical trajectory that intertwines botanical exploration and horticultural cultivation.
The journey of this species, from its native habitat to global horticultural prominence, is marked by several key milestones:
- 18th-century discovery: Documented by European botanists during exploratory expeditions in South America.
- Taxonomic classification: Initially classified under the genus Philodendron, highlighting its unique morphological traits.
- Victorian era popularity: Gained traction as an ornamental plant in European botanical gardens.
- 20th-century hybridization: Intensified cultivation efforts led to numerous hybrids and cultivars.
- Modern-day status: Continues to be a favorite among plant enthusiasts worldwide for its aesthetic appeal and adaptability.
These historical developments underscore the plant's enduring significance in botanical and horticultural circles.
Botanical Characteristics
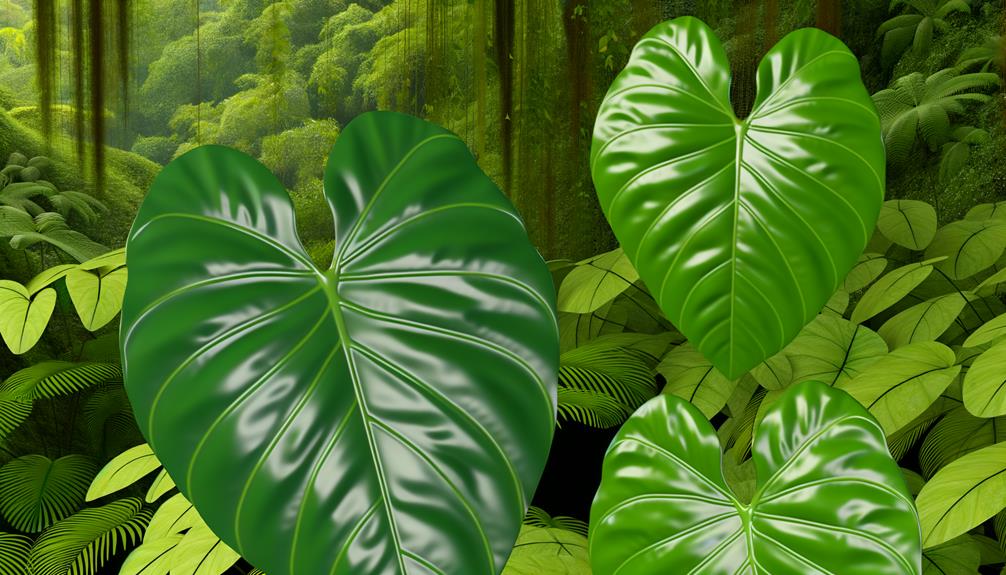

The Philodendron cordatum, characterized by its distinctive heart-shaped leaves and aerial roots, exhibits a range of morphological features that make it a subject of interest in both botanical studies and horticultural practices.
Its leaves, typically measuring 10-20 cm in length, display a glossy, deep green hue with prominent venation. The plant's growth habit is primarily vining, facilitated by its aerial roots which anchor to surfaces, aiding in nutrient absorption. Stem internodes are relatively short, promoting dense foliage.
Additionally, the inflorescence consists of a spadix and spathe, common to many Araceae family members. The plant's adaptability to low light conditions and ease of propagation via stem cuttings contribute to its popularity among indoor plant enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Common Misidentifications
Philodendron cordatum is frequently misidentified due to its morphological similarities with other species such as Philodendron hederaceum and Epipremnum aureum. This issue is exacerbated by inaccurate labeling in commercial nurseries and retail stores.
Accurate identification hinges on detailed examination of leaf shape, venation patterns, and growth habits.
Similar-Looking Plant Species
Among the various species that resemble Philodendron cordatum, Hederagenus (English ivy) and Epipremnum aureum (Pothos) are frequently misidentified due to their similar heart-shaped leaves and vining growth habit.
Distinguishing these species involves scrutinizing specific morphological characteristics:
- Leaf Texture: Philodendron cordatum leaves are matte, whereas Pothos leaves exhibit a glossy sheen.
- Venation Pattern: Philodendron cordatum has a more pronounced and consistent venation compared to the random pattern in Pothos.
- Growth Habit: English ivy tends to climb vertically, adhering to surfaces with aerial rootlets, unlike the more sprawling nature of Philodendron cordatum.
- Petiole Shape: Philodendron's petioles are rounder, whereas Pothos petioles are more flattened.
- Aerial Roots: English ivy features more numerous, finer aerial roots than Philodendron cordatum.
Mislabeling in Stores
In retail environments, mislabeling of Philodendron cordatum is prevalent, often leading to confusion among consumers and improper care practices. This issue arises primarily due to the morphological similarities between Philodendron cordatum and other species such as Philodendron hederaceum and Philodendron scandens.
Retailers frequently misidentify these plants, labeling them interchangeably. Such inaccuracies can result in consumers applying incorrect horticultural practices, as different species may have varying light, water, and nutrient requirements.
Mislabeling also complicates botanical research and conservation efforts, as the precise identification of plant species is paramount for accurate data collection and analysis. Consequently, enhancing retailer education on plant taxonomy and improving labeling systems can mitigate these challenges, ensuring better consumer outcomes and scientific integrity.
Identifying Key Differences
One important aspect of distinguishing Philodendron cordatum from its commonly misidentified counterparts involves examining the leaf morphology, including shape, size, and venation patterns. This species can often be confused with other Philodendrons, such as Philodendron hederaceum and Philodendron oxycardium. Identifying key differences requires close observation:
- Leaf Shape: Philodendron cordatum typically has more heart-shaped leaves.
- Leaf Size: The leaves are generally smaller and more uniform in size.
- Venation Patterns: Prominent primary veins with less conspicuous secondary veins.
- Petiole Characteristics: Thinner and sometimes slightly grooved petioles.
- Growth Habit: Exhibits a vining growth form with internodes that are relatively longer.
These morphological markers are critical for accurate identification and avoiding common misidentifications.
Importance of Scientific Names

Utilizing scientific names, like Philodendron cordatum, guarantees clear communication among researchers and horticulturists worldwide. These binomial nomenclatures, established by the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), offer a standardized linguistic framework.
This precision eliminates confusion arising from common names, which can vary significantly across different languages and regions. Scientific names also encapsulate phylogenetic relationships, aiding in the classification and identification of plant species. For instance, the genus Philodendron encompasses numerous species, and the specific epithet 'cordatum' precisely denotes this particular heartleaf variety.
Additionally, these names facilitate accurate documentation, ensuring consistency in botanical research, conservation efforts, and horticultural practices. Therefore, scientific nomenclature is indispensable for maintaining clarity and universal understanding in plant sciences.
Tips for Plant Identification
Recognizing the significance of scientific nomenclature, plant identification involves several key techniques to accurately distinguish species, such as examining morphological characteristics, leaf patterns, and growth habits. Detailed analysis of these features allows for precise classification and differentiation.
Effective plant identification strategies include:
- Leaf Morphology: Evaluating size, shape, edge type, and arrangement.
- Stem Structure: Observing the presence of nodes, internodes, and stem composition.
- Flower Characteristics: Identifying petal arrangement, color, and reproductive structures.
- Growth Habit: Noting whether the plant is climbing, trailing, or upright.
- Root System: Inspecting root type, depth, and spread.
Each of these aspects provides critical insights into the plant's taxonomy, facilitating accurate species identification essential for scientific research and horticultural practices.
Conclusion
To sum up, Philodendron cordatum, scientifically referred to as Philodendron hederaceum, continues to be a topic of botanical interest because of its distinctive taxonomy and morphological traits. Despite frequent misidentifications, precise scientific naming is essential for efficient communication among scholars.
Detractors may claim that vernacular names are adequate; nonetheless, the accuracy of scientific terminology guarantees lucidity and uniformity. As a result, grasping and employing the accurate scientific name enriches the capacity to examine, protect, and value this species within its ecological setting.






