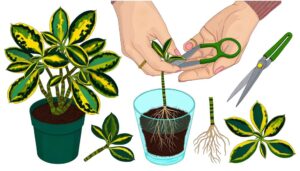
Propagate Philodendron B
To propagate Philodendron B, begin by selecting a healthy parent plant free of diseases and pests. Use sterilized pruning shears to cut a 4-6 inch stem section, ensuring it has at least one node.
Dip the cut end in rooting hormone. For water propagation, submerge the node in distilled water, changing it every 5-7 days.
For soil propagation, plant the cutting in a well-draining medium composed of peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite. Maintain high humidity and consistent moisture levels.
Monitor root development, typically initiating within 2-3 weeks. Interested in optimizing conditions for rapid growth?

Key Takeaways
- Select healthy, disease-free parent plants in active growth phase, preferably in spring or summer.
- Use sterilized pruning shears to take 4-6 inch cuttings with at least one node and multiple leaves.
- Apply rooting hormone to the cut end for improved root development before planting.
- Use a well-draining propagation medium like perlite or vermiculite and keep it consistently moist.
- Maintain high humidity with a humidity dome or plastic bag and monitor for root initiation within 2-3 weeks.
Choosing Healthy Parent Plants
Selecting robust and disease-free parent plants is critical for successful propagation of Philodendron B. Begin by examining the morphological characteristics, ensuring the plant exhibits vigorous growth, vibrant foliage, and absence of chlorosis or necrosis.
Assess the root system for signs of rot or pest infestation, which could compromise the integrity of cuttings. Conduct a phytosanitary inspection to ascertain the absence of pathogenic organisms such as fungi, bacteria, and viruses.
Opt for specimens with strong apical dominance, as these will produce more viable cuttings. Additionally, verify that the parent plant is in its active growth phase, typically during spring or summer, to enhance rooting success.
Ensuring the genetic and physiological health of the parent plant underpins effective propagation outcomes.
Gathering Necessary Tools
After securing the health and vitality of the parent Philodendron B plants, the next step involves gathering the necessary propagation tools. Essential items include sterilized pruning shears, a clean, sharp knife, and rooting hormone powder to enhance root development.
Additionally, prepare a propagation medium comprising perlite, vermiculite, or a sterile potting mix to guarantee optimal aeration and drainage. Transparent plastic bags or a humidity dome are critical for maintaining high humidity levels during the rooting process.
Moreover, small pots or propagation trays should be sterilized to prevent pathogen introduction. A misting bottle filled with distilled water aids in maintaining moisture without over-saturation. Gathering these tools ensures a sterile, conducive environment for successful Philodendron B propagation.
Selecting the Right Season
Best propagation success for Philodendron B is achieved by initiating the process during the active growth phase, typically in the spring or early summer. During this period, the plant exhibits enhanced metabolic activity, which facilitates root development and foliage growth. To optimize conditions, monitor environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure. The following table provides essential parameters for successful propagation:
| Factor | Ideal Range |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 20-25°C (68-77°F) |
| Humidity | 60-70% |
| Light | Indirect, bright light |
| Watering | Keep soil consistently moist |
| Fertilization | Bi-weekly with balanced fertilizer |
Adhering to these conditions ensures the plant's physiological processes remain conducive to propagation, thereby increasing the likelihood of successful root and shoot development.
Identifying Ideal Cuttings
To guarantee successful propagation of Philodendron B, it is vital to select cuttings from healthy, vigorous stems exhibiting no signs of disease or pest infestation.
Best cuttings should include at least one node, the anatomical region where leaf and root development originates. Accurate identification and selection of these nodes are essential, as they greatly influence the rooting success and overall viability of the new plant.
Healthy Stem Selection
Selecting a healthy stem for propagation necessitates identifying cuttings that exhibit robust growth, free from disease or pest infestation, and possess at least two to three nodes where root development can initiate. Begin by examining the parent plant for stems with firm texture and vibrant coloration, indicative of vigorous health.
Avoid stems exhibiting discoloration, wilting, or signs of pathogen presence, as these are prone to unsuccessful propagation. Utilize sterilized pruning shears to make a clean cut just below a node, ensuring minimal tissue damage.
Optimal cuttings are typically 4-6 inches long, containing multiple leaves to sustain photosynthesis while roots establish. This meticulous selection process enhances the likelihood of successful propagation, fostering resilient new plants.
Node Identification
Accurately identifying nodes is essential for successful philodendron propagation. Nodes are the specific points on the stem where root development initiates. They are discernible by the presence of small, brownish or whitish bumps, often located where a leaf or petiole connects to the stem.
For best rooting results, select cuttings that include at least one node and one healthy leaf. Utilize sterilized pruning shears to make precise cuts just below the node, ensuring minimal tissue damage. Avoid sections with visible signs of disease or pest infestation.
Proper node identification and clean cutting techniques greatly enhance the likelihood of successful root formation and robust plant growth, thereby improving the propagation process.
Making the Cut
To initiate the cutting process, first identify the perfect cutting location by targeting a stem segment that includes at least one node and two to three leaves.
Equip yourself with sterilized, sharp pruning shears to guarantee accuracy and minimize tissue damage.
Execute the cut at a 45-degree angle just below the node to facilitate ideal rooting and nutrient uptake.
Ideal Cutting Location
Identifying the best cutting location on a Philodendron B involves locating a node that exhibits strong growth, typically characterized by the presence of aerial roots or visible leaf buds. Nodes are essential as they contain meristematic tissues which are responsible for the development of new roots and shoots.
Aerial roots, often emerging from nodes, indicate active growth and vitality, making them ideal for propagation. When selecting a cutting, make sure the node is healthy, devoid of any signs of disease or pest infestation.
Position the cut approximately 1-2 centimeters below the chosen node to preserve its integrity. This strategic placement not only enhances the likelihood of successful root development but also minimizes potential damage to the parent plant.
Necessary Tools Preparation
Before making the cut, verify all necessary tools are carefully sterilized to prevent any bacterial or fungal contamination. Proper preparation of tools is crucial to ensure best plant health and successful propagation. Utilize a 70% isopropyl alcohol solution to disinfect the instruments thoroughly.
Essential tools include:
- Sharp Pruning Shears: Ensuring clean, precise cuts to minimize tissue damage.
- Sterilized Scalpel: For making smaller or more intricate incisions.
- Disinfectant Solution: For consistent sterilization between multiple cuts or plants.
Confirm that each tool is in excellent condition and has been sharpened adequately to facilitate a smooth cut. This thorough preparation minimizes the risk of infection and promotes the rapid formation of healthy roots in the propagated Philodendron B.
Ensuring Clean Cuts
Secure the cutting angle is precise and clean by positioning the sterilized pruning shears or scalpel at a 45-degree angle, targeting a node where new root growth will initiate. This angular cut increases the surface area for rooting, enhancing water and nutrient uptake. Confirm tools are sterilized to mitigate pathogen transmission. Execute a swift, decisive cut to minimize tissue damage and promote healthy regrowth.
| Tool | Angle | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Pruning Shears | 45° | Maximize rooting surface |
| Scalpel | 45° | Precision cutting |
| Sterilization Agent | N/A | Pathogen prevention |
Following these steps meticulously will significantly improve the success rate of Philodendron B propagation, ensuring robust and vigorous new plant development.
Preparing Cuttings for Planting
Optimizing growth conditions begins with selecting healthy stems, ideally 4-6 inches in length, from a mature Philodendron B plant.
To enhance the cuttings for planting, follow these specific steps. First, eliminate any lower leaves to prevent rot and disease.
Next, confirm at least one node, the part where leaves attach, is included in each cutting, as this is the primary site for root development.
Finally, allow the cuttings to air dry for a few hours to form a callus over the cut surface, which minimizes infection risk.
These steps are essential for successful propagation.
Rooting in Water
For successful rooting in water, make sure that cuttings are prepared with at least one node submerged to facilitate root development. Utilize distilled or filtered water to minimize contaminants, and maintain peak oxygenation by changing the water every 5-7 days.
Monitor for root initiation, typically occurring within 2-3 weeks, adjusting care protocols as needed.
Cutting Preparation Essentials
To prepare your Philodendron B cuttings for rooting in water, begin by selecting healthy, mature stems with at least two to three nodes and a few leaves. Utilize sterilized pruning shears to make a clean cut just below a node, guaranteeing minimal tissue damage. Remove any lower leaves to prevent submersion, which can lead to rot.
Submerge the cut end in a container filled with chlorine-free, room-temperature water, ensuring nodes are fully covered but leaves remain dry.
Confirm the container is transparent to monitor root development.
Position the container in indirect sunlight to prevent algae growth and promote photosynthesis.
Change the water periodically to maintain oxygen levels and prevent bacterial build-up.
This precise preparation promotes vigorous root formation.
Water Change Frequency
Maintaining best water quality is important during the propagation process, requiring regular water changes to prevent stagnation and bacterial growth. For ideal root development, it is recommended to change the water every 3-4 days.
Use distilled or filtered water to avoid chlorine and other contaminants that may hinder root formation. Keep the water at room temperature to provide a stable environment for the cuttings.
During each water change, thoroughly rinse the container to eliminate any biofilm accumulation. Additionally, inspect the cuttings for signs of rot and promptly remove affected sections to prevent the spread of pathogens.
Consistent water changes will enhance oxygenation, promoting healthier and more robust root development in Philodendron B cuttings.
Rooting in Soil
Rooting Philodendron B cuttings in soil requires selecting a well-draining, nutrient-rich potting mix to achieve best growth conditions. The following steps are recommended for prime root development:
- Preparation: Utilize a potting mix composed of equal parts peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite to guarantee adequate aeration and moisture retention.
- Planting: Insert the cutting into the soil up to the node, guaranteeing the node is covered to facilitate root emergence.
- Moisture Management: Maintain consistent soil moisture by lightly watering the cutting, avoiding waterlogged conditions to prevent root rot.
Ensuring Proper Conditions
Ideal conditions for rooting Philodendron B cuttings encompass precise humidity levels, sufficient light exposure, and stable temperature ranges.
The best humidity should be maintained between 70-80%, achievable through the use of a humidity dome or misting apparatus.
Adequate light exposure is vital; provide indirect, diffused sunlight for 10-12 hours per day to facilitate photosynthetic activity without causing photodamage.
Temperature stability is essential, with an ideal range of 70-75°F (21-24°C). Fluctuations beyond this range can impede root development. Utilize a heating mat if necessary to maintain consistent warmth.
Additionally, make sure the growing medium remains adequately moist but not waterlogged to prevent root rot. These conditions collectively foster an environment conducive to successful rooting.
Monitoring Growth Progress
To accurately monitor the growth progress of Philodendron B cuttings, regularly assess root development and overall plant vigor using a combination of visual inspections and quantitative measurements. This involves:
- Root Examination: Gently remove the cutting from its medium to inspect root length, density, and health. Look for white, firm roots indicating healthy growth.
- Leaf Evaluation: Monitor new leaf emergence and existing leaf health. Chlorosis or necrosis could indicate underlying issues.
- Growth Measurements: Record quantitative data such as root length in centimeters and new leaf count weekly. This enables tracking progress and identifying stagnation.
Employing these methods ensures that the propagation process is on track, providing valuable insights into the best conditions for Philodendron B cuttings.
Transplanting Rooted Cuttings
Once the Philodendron B cuttings have developed a robust root system, characterized by numerous white, firm roots, they are ready for transplantation into a more permanent growing medium.
Begin by selecting a well-draining potting mix, preferably one comprising peat moss, perlite, and orchid bark to guarantee ideal aeration and moisture retention.
Prepare a container with adequate drainage holes to prevent waterlogging. Gently remove the cuttings from their propagation medium, taking care to minimize root disturbance.
Position the cutting in the new medium, ensuring the root ball is fully covered. Lightly tamp the soil to secure the cutting in place. Water thoroughly to settle the soil around the roots.
Guarantee the transplanted cuttings receive indirect light and maintain moderate humidity levels.
Caring for New Plants
Ensuring the health and strength of newly transplanted Philodendron B plants necessitates meticulous attention to their specific environmental and nutritional requirements. Optimum care involves regulating light, moisture, and soil conditions to support robust growth and development.
- Light Requirements: Position the plants in indirect sunlight to prevent leaf scorching while ensuring adequate photosynthetic activity.
- Moisture Control: Maintain consistent soil moisture by watering when the top inch of soil is dry, avoiding waterlogging to prevent root rot.
- Nutritional Needs: Administer a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer bi-weekly to provide essential macro and micronutrients, promoting vigorous growth.
Each of these elements plays a critical role in fostering a conducive environment, ensuring that Philodendron B plants thrive and maintain their ornamental appeal.
Conclusion
To wrap up, the meticulous propagation of Philodendron bipinnatifidum, while appearing simple, requires a significant effort in plant parent selection, precise techniques in cuttings, and a steadfast dedication to ideal growth conditions.
The irony, naturally, is that this laborious procedure is carried out for a plant that is frequently commended for its easy-care characteristics.
Consequently, the propagation of such a seemingly uncomplicated plant unveils the delicate balance between botanical science and horticultural creativity.