Philodendron Xanadu Vs Selloum
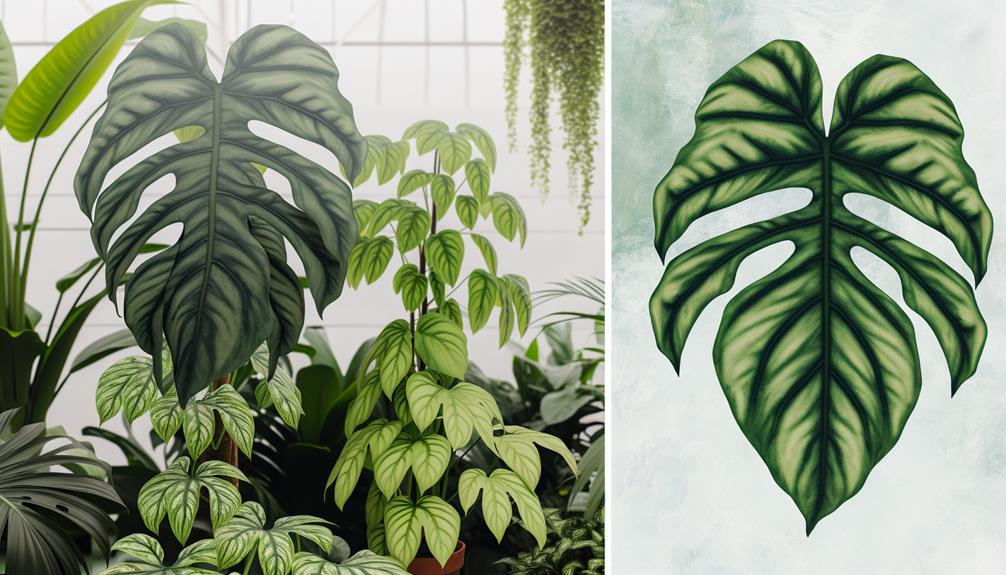
Philodendron Xanadu and Philodendron Selloum display distinct morphological differences. Xanadu features compact, deeply lobed leaves and maintains a bushier growth habit, reaching 2-4 feet in height.
In contrast, Selloum shows larger, elongated leaves with extensive lobation and can grow up to 10 feet tall, adopting a more tree-like structure. Xanadu thrives in well-drained, slightly acidic to neutral soils, while Selloum prefers loamy or sandy soils with moderate organic matter.
Both species require bright, indirect light and meticulous watering practices to avoid root rot and promote optimal health. For a detailed examination of their unique characteristics, further inquiry will be advantageous.

Key Takeaways
- Philodendron Xanadu has compact, symmetrical, deeply lobed leaves, while Selloum features larger, irregularly lobed leaves with a rugged appearance.
- Xanadu grows up to 2-4 feet tall, whereas Selloum can reach up to 10 feet tall with a 6-8 feet spread.
- Selloum has a tree-like structure with elongated, broad leaves, while Xanadu maintains a bushier, dense, shrubby appearance.
- Both thrive in bright, indirect light, but inadequate light can cause leggy growth, and excessive direct sunlight may lead to leaf burn.
- Xanadu prefers well-drained, slightly acidic to neutral soil, and Selloum thrives in loamy or sandy soil with good drainage.
Appearance and Structure
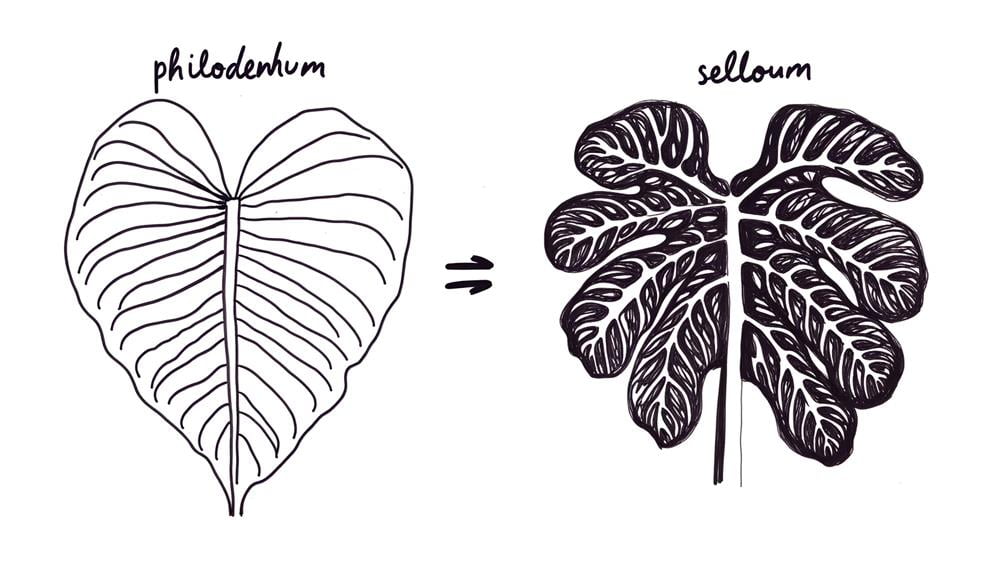
Philodendron Xanadu and Philodendron Selloum exhibit distinct morphological characteristics, with Xanadu featuring more compact, deeply lobed leaves and a bushier growth habit, while Selloum presents larger, more elongated leaves with an expansive, tree-like structure.
Xanadu's leaves are typically dark green, deeply incised, and smaller, contributing to its dense, shrubby appearance. In contrast, Selloum's leaves are broader, showcasing a more pronounced and extensive lobation pattern, often giving rise to a more open and airy canopy.
The petioles of Selloum are robust and longer, supporting its larger foliage. Additionally, Selloum's stems are thicker and more lignified, indicative of its semi-arborescent nature. These structural differences underscore their unique adaptations and suitability for varied horticultural applications.
Growth Habits
Growth habits in Philodendron Xanadu and Philodendron Selloum manifest distinct variations in leaf morphology, overall dimensions, and photic responses.
These species exhibit differential leaf shape characteristics, with Xanadu presenting lobed leaves and Selloum showcasing deeply dissected leaves.
Additionally, their respective size, spread, and light requirements underscore their adaptation strategies and ecological niches.
Leaf Shape Differences
The leaf morphology of Philodendron Xanadu and Selloum, though superficially similar, exhibits distinct differences that reflect their unique growth habits and ecological adaptations.
Philodendron Xanadu displays compact, deeply lobed leaves with a more symmetrical, uniform structure. These leaves are typically smaller, with lobes extending from a central axis in a consistent pattern.
In contrast, Philodendron Selloum features larger, more irregularly lobed leaves, often with a more rugged or serrated appearance. The lobes of Selloum's leaves are more pronounced and can vary significantly in shape and size.
These morphological variations indicate Xanadu's adaptation to a more controlled environment, whereas Selloum exhibits traits suited for a broader ecological range, favoring more expansive growth.
Size and Spread
In exploring the dimensions and proliferation patterns of these two species, it becomes evident that Philodendron Xanadu maintains a more compact and controlled growth habit compared to the expansive and vigorous spread characteristic of Philodendron Selloum. Philodendron Xanadu typically reaches a height of approximately 2-4 feet with an equal spread, forming a dense, bushy appearance.
In contrast, Philodendron Selloum, also known as Philodendron bipinnatifidum, can attain heights of up to 10 feet with a spread extending 6-8 feet, often developing a tree-like structure. The rhizomatous growth of Xanadu guarantees a well-contained form, whereas Selloum exhibits a more aggressive lateral expansion through its extensive root system and larger petioles, resulting in a more sprawling morphology.
Light Requirements
Best lighting conditions are necessary for both Philodendron Xanadu and Philodendron Selloum, with each species showing distinct preferences that greatly impact their growth habits.
Philodendron Xanadu thrives in bright, indirect light, which promotes compact growth and vibrant foliage coloration.
Conversely, Philodendron Selloum, also known as Tree Philodendron, exhibits ideal growth under moderate to bright indirect light, tolerating lower light conditions than Xanadu.
Inadequate light for either species can result in leggy growth and diminished leaf size, while excessive direct sunlight may cause leaf burn and chlorosis. Understanding these light requirements is essential to cultivating healthy specimens, ensuring their morphological characteristics are maintained and their overall well-being is supported.
Proper light management thus directly influences their aesthetic and physiological development.
Light Requirements

Understanding the light requirements of Philodendron Xanadu and Selloum is essential for best growth and health. Philodendron Xanadu thrives in bright, indirect sunlight but exhibits a robust tolerance for partial shade, whereas Selloum prefers similar conditions yet may exhibit reduced foliage density in lower light environments.
Both species show adaptability to artificial light, although adjustments in intensity and duration are necessary to mimic their natural habitats effectively.
Optimal Sunlight Conditions
Both Philodendron Xanadu and Philodendron Selloum thrive under bright, indirect sunlight, although they can tolerate lower light conditions to some extent. Best sunlight conditions for these species involve exposure to filtered light, which prevents the direct impact of ultraviolet rays on their foliage. Direct sunlight can lead to photodamage, manifesting as leaf burn or chlorosis.
A position near east or north-facing windows is ideal, offering diffused light throughout the day. Artificial grow lights with a balanced spectrum can supplement natural light during shorter daylight periods.
Consistency in light exposure ensures strong photosynthetic activity, promoting healthy growth and vibrant leaf coloration. Maintaining adequate light without direct exposure is crucial for preserving the physiological health and aesthetic appeal of these ornamental plants.
Shade Tolerance Levels
While ideal sunlight conditions play a significant role in the health of Philodendron Xanadu and Philodendron Selloum, their adaptability to lower light environments showcases their remarkable shade tolerance levels.
Philodendron Xanadu, known for its compact growth and dense foliage, demonstrates moderate tolerance to partial shade, thriving in filtered light conditions.
In contrast, Philodendron Selloum exhibits a higher shade tolerance, maintaining robust growth even under low light conditions. This species can sustain its large, deeply lobed leaves with minimal light, making it suitable for shaded indoor environments.
The key difference lies in their leaf morphology and chlorophyll density, which enable Selloum to optimize photosynthesis efficiency under suboptimal light conditions, whereas Xanadu requires slightly brighter settings to sustain its compact form.
Artificial Light Adaptability
How do Philodendron Xanadu and Philodendron Selloum adapt to artificial light conditions, and what specific light requirements must be met to support their best growth?
Philodendron Xanadu exhibits a higher adaptability to low-intensity artificial light, thriving under fluorescent or LED lights with a spectrum close to natural daylight (4000-6500K). Conversely, Philodendron Selloum demands brighter artificial light conditions, preferably full-spectrum grow lights that mimic sunlight.
Both species necessitate approximately 12-14 hours of consistent light exposure daily. However, Xanadu's compact morphology enables efficient light absorption, whereas Selloum's expansive leaf structure requires more intense illumination to prevent etiolation.
Regular monitoring of light intensity using a light meter assures optimal growth and mitigates potential light-related stress.
Watering Needs
Understanding the distinct watering needs of Philodendron Xanadu and Selloum is necessary for maximizing their growth and health.
Philodendron Xanadu requires consistently moist soil but is highly vulnerable to root rot, requiring careful regulation of water to avoid waterlogged conditions.
In contrast, Philodendron Selloum exhibits a more resilient tolerance for varying moisture levels; however, it still benefits from a well-draining medium to prevent prolonged saturation.
Both species exhibit increased water requirements during active growth phases, typically in the warmer months.
Monitoring for signs of overwatering, such as yellowing leaves or soggy soil, is important for both plants.
Employing a structured watering schedule, adjusted seasonally, can mitigate common issues and promote optimal physiological functions.
Soil Preferences
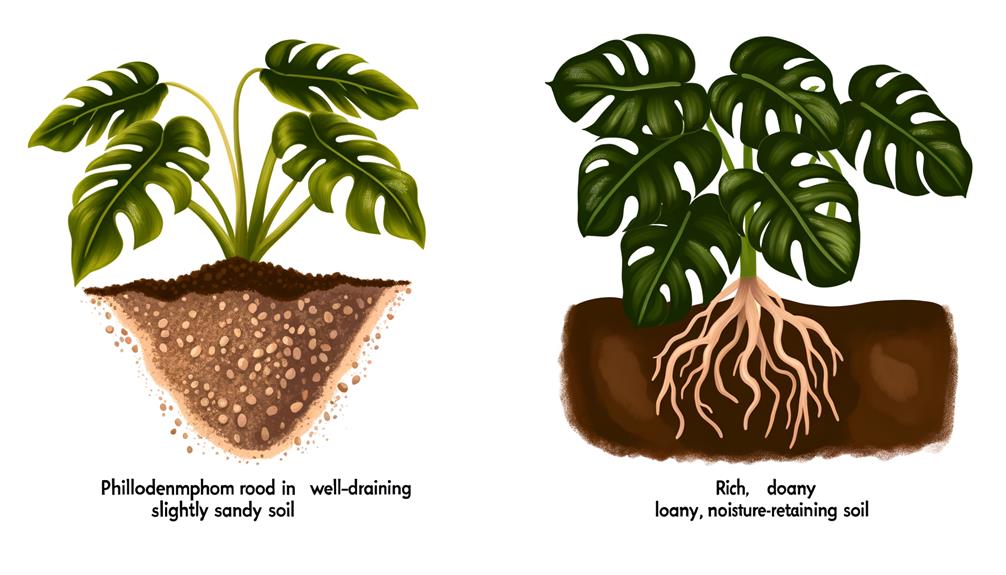
Philodendron Xanadu and Selloum each exhibit distinct soil preferences that are critical for their best growth and health. Xanadu thrives in well-drained, slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH of 6.0-7.0, enriched with organic matter. Selloum, on the other hand, prefers a loamy or sandy soil with good drainage and a slightly acidic pH range of 5.5-6.5. Both species benefit from soil aeration to prevent root rot and support nutrient uptake. Below is a comparative table summarizing these preferences:
| Characteristic | Philodendron Xanadu | Philodendron Selloum |
|---|---|---|
| pH Range | 6.0-7.0 | 5.5-6.5 |
| Soil Type | Well-drained, organic-rich | Loamy or sandy, well-drained |
| Organic Matter | High | Moderate |
| Aeration | Essential | Essential |
Understanding these soil requirements is crucial for optimal plant health and growth.
Common Issues
Both Philodendron Xanadu and Selloum are prone to common issues such as root rot, pest infestations, and nutrient deficiencies, which can greatly impact their health and growth.
Root rot, typically caused by overwatering or poorly draining soil, leads to discolored leaves and mushy roots.
Pest infestations, notably from spider mites and aphids, frequently result in stippled foliage and reduced vigor.
Nutrient deficiencies, particularly of nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium, manifest as chlorosis, stunted growth, and leaf deformities.
Regular monitoring and appropriate cultural practices, such as well-draining soil, balanced fertilization, and integrated pest management, are crucial for mitigating these issues.
Adopting these measures ensures the robust health and aesthetic appeal of both Philodendron Xanadu and Selloum.
Conclusion
To sum up, the comparative analysis of Philodendron xanadu and Philodendron selloum reveals distinct differences in morphology, growth patterns, and environmental preferences.
Xanadu exhibits a compact growth habit, while Selloum's structure is more expansive.
Both species require moderate light and consistent watering, yet their soil preferences diverge. Understanding these nuances is crucial for best cultivation.
The allure of these botanical marvels cannot be overstated; they are veritable champions in the world of ornamental horticulture, adding unparalleled aesthetic value to any collection.






