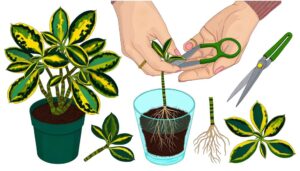
How to Propagate Philodendron Fat Boy? Easy Methods!
To propagate Philodendron ‘Fat Boy’, initiate the process during spring or early summer when growth is active. Maintain an environment with temperatures between 70-85°F, indirect bright light, and 60-70% humidity.
Utilize sterilized pruning shears and a rooting hormone. Select a healthy stem with robust root primordia and strong nodes.
Cut below the node, remove lower leaves, and plant in a well-draining medium comprising peat, perlite, and orchid bark. Bury the cut end, leaving leaves above the surface.
Water consistently, making sure the soil remains slightly dry between waterings. Monitoring the plant closely guarantees successful rooting and growth.
For detailed steps and advanced care, explore further.

Key Takeaways
- Propagate Philodendron Fat Boy in spring or early summer during active growth.
- Use sterilized shears to cut below a healthy node with aerial roots.
- Prepare a mix of peat, perlite, and orchid bark as the propagation medium.
- Bury the node in soil, ensuring stem and leaves remain above the surface.
- Maintain 70-85°F temperature, 60-70% humidity, and indirect bright light.
Choosing the Right Time
Selecting the best season for propagating Philodendron Fat Boy is crucial, as it greatly impacts the success rate and overall plant health. The prime period for propagation is typically during the spring and early summer months. During this time, the plant is in its active growth phase, thereby enhancing its ability to generate new roots and shoots efficiently.
Temperature and ambient light conditions are also critical; aim for a range between 70-85°F with indirect, bright light to foster optimal growth. Humidity should be maintained at 60-70% to mimic the plant’s natural tropical environment.
Avoid propagation during the dormant fall and winter periods, as reduced metabolic activity can significantly diminish propagation success rates. Proper timing guarantees robust, healthy development of new plants.
Gathering Necessary Tools
To guarantee a seamless propagation process for Philodendron Fat Boy, it is crucial to gather all necessary tools. These include sterilized pruning shears, rooting hormone, a clean container with drainage holes, and a well-draining potting mix.
Sterilized pruning shears facilitate clean cuts, reducing the risk of transmitting pathogens. Rooting hormone enhances root development, increasing the success rate of propagation.
Selecting a container with adequate drainage prevents waterlogging, which can lead to root rot. Utilizing a well-draining potting mix, ideally one containing perlite or orchid bark, provides optimal aeration and moisture retention, creating an ideal environment for root growth.
Having these tools ready will streamline the propagation process, ensuring that each step can be executed with accuracy and efficiency.
Selecting a Healthy Stem
When selecting a healthy stem for propagation, it is important to identify strong nodes, as these are the sites where new roots will form.
Additionally, a thorough inspection for pests is necessary to guarantee the selected stem is free from infestations that could hinder growth.
These preparatory steps are vital for successful Philodendron Fat Boy propagation.
Identifying Strong Nodes
In identifying strong nodes for propagation, it is important to examine the stem for well-developed, active growth points where leaves and roots converge. This guarantees the segment selected will have the necessary strength to establish new growth.
A thorough evaluation of the nodes is crucial. Look for the following characteristics:
- Prominent Root Primordia: Small, nub-like structures indicating potential root development.
- Healthy Leaf Attachment: Firmly attached leaves that are not wilted or yellowing.
- Sturdy Stem Integrity: A robust stem that is free from any signs of damage or rot.
These indicators are essential for selecting a segment that has the highest likelihood of successful propagation. Confirming these factors are present will greatly enhance the chances of cultivating a thriving Philodendron Fat Boy.
Checking for Pests
After identifying strong nodes, it is pivotal to make sure the selected stem is free from pests to prevent future infestations and promote healthy growth. Begin by closely inspecting the stem and its leaves for signs of common pests such as aphids, spider mites, and mealybugs.
Utilize a magnifying glass to detect minute insects and eggs, often found on the undersides of leaves and at nodes. Look for indicators like webbing, honeydew, or discolored spots, which may suggest pest presence.
If pests are detected, treat the plant with appropriate insecticidal soap or neem oil before propagation. Ensuring a pest-free stem enhances the likelihood of successful propagation and prevents the spread of infestations to other plants.
Making the Cut
When making the cut, it is crucial to select a node that shows healthy growth and is free from any signs of disease or pest infestation.
Prior to making any incisions, verify that all cutting tools are thoroughly sterilized to prevent the introduction of pathogens.
This methodical approach minimizes the risk of contamination and enhances the likelihood of successful propagation.
Choosing the Node
To guarantee successful propagation of Philodendron Fat Boy, it is important to select a healthy node that exhibits at least one aerial root and robust stem structure. The node is the critical juncture where new growth will emerge; its selection should be meticulous.
When choosing the node, consider the following attributes:
- Aerial Roots: Confirm that the node has at least one healthy aerial root, as this indicates active growth and increases the likelihood of successful propagation.
- Stem Integrity: The stem should be free from blemishes, scars, or signs of disease, ensuring that it can support new growth.
- Leaf Presence: Nodes with one or two leaves attached are preferable, as they facilitate photosynthesis and provide energy during root development.
This methodical approach is essential for best results.
Sterilizing Cutting Tools
Making sure that all cutting tools are properly sterilized is vital to prevent the introduction of pathogens to the Philodendron Fat Boy, thereby safeguarding the plant’s health during propagation.
Begin by selecting high-quality, sharp pruning shears or a sterilized knife to guarantee a clean cut. Utilize a disinfectant solution, such as isopropyl alcohol (70% concentration) or a bleach solution (1 part bleach to 9 parts water), to sterilize the tools.
Immerse the cutting edges in the solution for at least 30 seconds, ensuring complete contact with the disinfectant. Rinse thoroughly with sterile water to remove any residual chemicals. Dry the tools using a sterile cloth before making the cut.
This meticulous approach minimizes the risk of infection, promoting successful propagation.
Preparing the Cutting
Prior to making any cuts, it is crucial to select a healthy, mature Philodendron ‘Fat Boy’ specimen that exhibits robust growth and disease-free foliage. This guarantees the cutting will have the best chance of successful propagation.
Identify a section of the plant that includes a node, as this is where new roots will develop. Nodes appear as small bumps or rings along the stem.
Using sterilized cutting tools, follow these steps meticulously:
- Locate a node: Choose a stem section with at least one visible node.
- Make the cut: Cut about 1/4 inch below the node, ensuring a clean, precise incision.
- Remove lower leaves: Strip any leaves near the cut end, leaving a few at the top for photosynthesis.
This preparation is crucial for optimal root development.
Rooting in Water
After preparing the cutting, the next step involves placing the cut section into a container of clean, lukewarm water to initiate root development. Guarantee that the water level adequately covers the node, as this is where root formation will primarily occur.
It is crucial to maintain a consistent water temperature and quality; replace the water every few days to prevent stagnation and bacterial growth. Position the container in a location with indirect sunlight to provide ideal conditions for root emergence.
Monitor the cutting regularly for signs of root growth, which generally appear within two to four weeks. Properly managed, this method enhances root proliferation and prepares the cutting for the eventual shift to a soil medium.
Transplanting to Soil
Once the roots have developed to a length of approximately 2-3 inches, it is time to shift the Philodendron Fat Boy cutting from water to a well-draining soil medium. Select a pot with drainage holes to prevent waterlogging and root rot.
Prepare a soil mix rich in organic matter, making sure it retains moisture while providing aeration.
- Potting Soil: Use a mix containing peat, perlite, and orchid bark to guarantee sufficient drainage and nutrient retention.
- Planting Depth: Place the cutting in the soil so that the rooted section is completely buried but the stem and leaves remain above the surface.
- Watering: Provide a consistent watering schedule, allowing the top inch of soil to dry out between waterings to prevent over-saturation.
This method ensures ideal transplant success.
Conclusion
The successful propagation of Philodendron ‘Fat Boy’ hinges on the precise timing, careful selection of a healthy stem, and meticulous preparation of the cutting.
Coincidentally, the symbiotic relationship between the plant’s physiological state and environmental conditions underscores the importance of methodological adherence.
Rooting in water followed by transplantation to soil guarantees peak root development and stability.
Mastery of these techniques not only enhances growth but also contributes to a deeper understanding of plant propagation dynamics.