Why Does My Philodendron Brasil Have Pink Leaves?
Philodendron Brasil may display pink leaves due to genetic mutations disrupting chlorophyll synthesis and carotenoid accumulation. Environmental factors such as insufficient light exposure, nutrient imbalances (e.g., nitrogen or phosphorus deficiency), and inconsistent watering can impact pigmentation.
In addition, temperature extremes outside the ideal 65°F to 80°F range and pest infestations like spider mites can further contribute to abnormal leaf coloration. Ensuring proper light, balanced nutrients, stable temperatures, and diligent pest management is essential for maintaining healthy pigment production.
Exploring these factors in depth will provide further insights into managing and preventing pink leaves in your Philodendron Brasil.
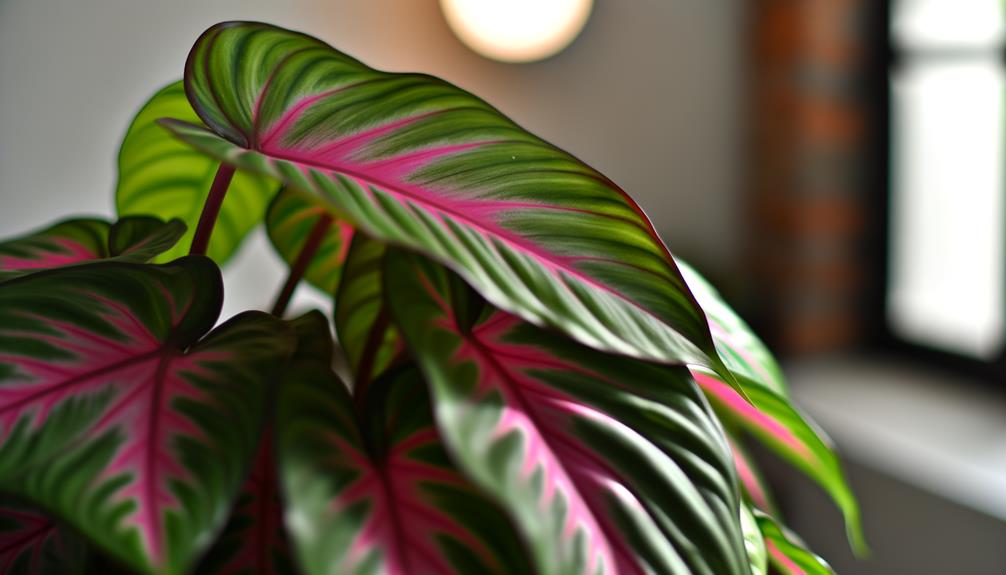

Key Takeaways
- Genetic mutations can alter chlorophyll synthesis, leading to pink leaves.
- Insufficient light exposure causes diminished pigmentation, resulting in pink hues.
- Nutrient imbalances, especially nitrogen deficiency, can cause atypical pigmentation and pink leaves.
- Overwatering or underwatering disrupts chlorophyll production, leading to pink leaves.
- Temperature fluctuations outside the 65°F to 80°F range can affect chlorophyll synthesis, causing pink leaves.
Genetic Mutations
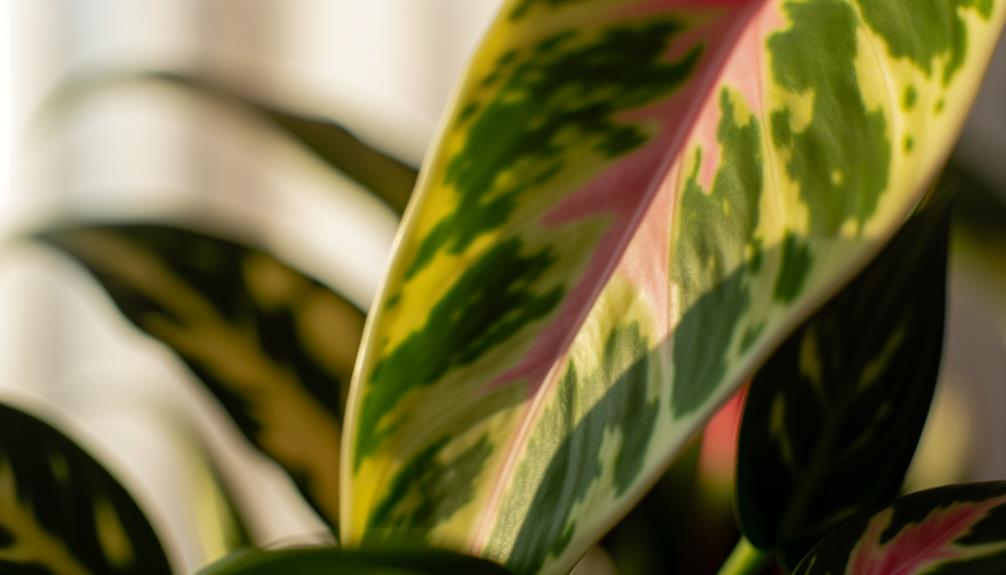

Genetic mutations in Philodendron Brasil, particularly those affecting pigmentation pathways, lead to the emergence of unusual pink leaves. These mutations often involve alterations in genes regulating chlorophyll synthesis and carotenoid accumulation.
A notable example is the disruption in the chloroplast development sequence, which impacts the green pigment production, resulting in a pink hue due to the relative visibility of anthocyanins.
Additionally, mutations can affect the expression of enzymes such as phytoene synthase and lycopene β-cyclase, which are pivotal in the biosynthesis of carotenoids.
The resultant phenotypic variation is not only an aesthetically intriguing trait but also provides a unique model for studying plant developmental biology and the intricate network of genetic controls underlying pigmentation.
Light Exposure
Light exposure plays a pivotal role in the phenotypic expression of Philodendron Brasil's pink leaves, with insufficient light leading to diminished pigmentation and less than ideal growth.
Ideal light conditions, typically bright, indirect sunlight, are essential for maintaining the plant's distinctive coloration and overall health.
Adjusting light levels to avoid both excessive direct sunlight and inadequate lighting is vital for achieving the desired aesthetic and physiological outcomes.
Insufficient Light Impact
Insufficient light exposure hinders the photosynthetic efficiency of Philodendron Brasil, leading to diminished chlorophyll production and the subsequent fading of its vibrant pink leaves.
Photoreceptors in the plant's cells require adequate light to drive photosynthesis, a process essential for synthesizing carbohydrates and maintaining chlorophyll levels. Without sufficient light, the plant cannot produce enough chlorophyll, resulting in color loss and paler foliage.
The variegation in Philodendron Brasil is particularly susceptible to light deficiencies, as the pink pigmentation indicates areas with reduced chlorophyll. Hence, insufficient light leads to a shift in pigmentation balance, causing the leaves to appear less vibrant.
This physiological stress not only impacts aesthetic appeal but also overall plant health and vigor.
Optimal Light Conditions
To counteract the adverse effects of insufficient light, it is vital to provide Philodendron Brasil with ideal light conditions that enhance its photosynthetic activity and sustain the vibrancy of its pink leaves.
Best light exposure entails bright, indirect sunlight, which supports chlorophyll production without causing photoinhibition. This balance promotes efficient energy conversion while preventing leaf burn. Light wavelengths in the blue and red spectra are necessary, promoting vegetative growth and pigmentation, respectively.
Utilizing a light meter can help maintain an intensity of 100-200 foot-candles, ensuring consistent light availability. Additionally, rotating the plant periodically ensures even light distribution, preventing etiolation and color fading.
These measures are essential for maintaining the physiological health and aesthetic appeal of Philodendron Brasil.
Adjusting Light Levels
Ensuring ideal light exposure for Philodendron Brasil involves meticulously adjusting light levels to match the plant's specific photosynthetic requirements. Best light conditions directly influence chlorophyll synthesis, essential for maintaining the plant's characteristic green and yellow variegation. Insufficient light can lead to etiolation, causing the leaves to develop a pink hue due to decreased chlorophyll concentration. Conversely, excessive light may cause photoinhibition, leading to leaf scorch and pigment alteration.
To maintain optimum conditions, consider the following light levels:
| Light Level | Impact on Philodendron Brasil |
|---|---|
| Low Light | Increased pink leaf pigmentation |
| Medium, Indirect Light | Balanced variegation and health |
| High, Direct Light | Potential leaf scorch and damage |
Adjusting light exposure based on these parameters ensures the plant's health and aesthetic integrity.
Nutrient Imbalance

A nutrient imbalance, particularly involving essential macronutrients and micronutrients, can greatly impact the coloration and overall health of Philodendron Brasil leaves.
Deficiencies in nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium often manifest as discoloration, including unusual pink hues. Nitrogen is essential for chlorophyll production and overall leaf greenness; a deficiency can lead to chlorosis and atypical pigmentation.
Phosphorus is crucial for energy transfer within the plant, affecting growth and leaf coloration, while potassium regulates various physiological processes, including water uptake and enzyme activation.
Micronutrients like iron, magnesium, and calcium also play vital roles in maintaining leaf health. Insufficient levels can disrupt chloroplast function and pigment synthesis, leading to the manifestation of unexpected colors, such as pink, in the foliage.
Watering Issues
In addition to nutrient imbalances, improper watering practices can greatly influence the appearance and health of Philodendron Brasil leaves, potentially leading to pink discoloration. Overwatering can cause root rot, impairing the plant's ability to uptake essential nutrients, thereby disrupting chlorophyll production which may manifest as pinkish hues.
Conversely, underwatering stresses the plant, leading to dehydration and nutrient transport issues that also affect pigmentation. The best watering regimen involves maintaining consistently moist, but not waterlogged, soil. It is vital to guarantee proper drainage to prevent water accumulation at the root zone.
Regularly monitor soil moisture levels and adjust watering frequency based on environmental conditions, thereby ensuring the physiological and biochemical processes essential for maintaining healthy leaf coloration are not compromised.
Temperature Fluctuations
Temperature fluctuations can profoundly affect the physiological processes in Philodendron Brasil, potentially leading to stress-induced pink discoloration of the leaves. Sudden changes in ambient temperature can disrupt cellular homeostasis, impairing chlorophyll synthesis and causing anthocyanin accumulation, which manifests as pink hues.
The most suitable temperature range for Philodendron Brasil is between 65°F to 80°F (18°C to 27°C). Exposure to temperatures below or above this range can induce abiotic stress, triggering defensive responses that alter pigment production. Additionally, rapid temperature shifts can impede nutrient uptake and water transport, exacerbating leaf discoloration.
Ensuring a stable temperature environment mitigates stress responses and maintains the plant's physiological equilibrium, thereby preserving its characteristic green and yellow variegation.
Pests and Diseases
Philodendron Brasil Pink Leaves are susceptible to various pests such as spider mites, aphids, and mealybugs, which can greatly impact their health. Identifying disease symptoms early, such as chlorosis, necrosis, and stunted growth, is crucial for effective management.
Implementing targeted treatment methods, including insecticidal soaps and systemic fungicides, can mitigate these issues and promote plant health.
Common Pest Infestations
An important aspect of maintaining the health of Philodendron Brasil Pink Leaves involves vigilant monitoring for common pest infestations such as spider mites, aphids, and mealybugs, which can compromise the plant's vitality and aesthetic appeal.
Spider mites (Tetranychidae) can cause stippling and discoloration by puncturing leaf cells to feed on their contents. Aphids (Aphidoidea) excrete a sticky honeydew that fosters sooty mold, hindering photosynthesis. Mealybugs (Pseudococcidae) form cotton-like masses on leaf axils and stems, extracting sap and introducing further plant stress.
Regular inspection and early intervention, including mechanical removal and the application of horticultural oils or insecticidal soaps, are important to mitigate these pests' impact and maintain the continued vibrancy and health of the Philodendron Brasil.
Disease Symptoms Identification
Identifying disease symptoms in Philodendron Brasil Pink Leaves involves recognizing signs such as chlorosis, necrotic lesions, and wilting, which can indicate underlying issues related to both pests and pathogenic infections. Chlorosis, or yellowing leaves, often suggests nutrient deficiencies or root damage, while necrotic lesions can signal fungal or bacterial infections. Wilting, despite adequate watering, typically points towards root rot or vascular pathogens.
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Chlorosis | Nutrient deficiency, root damage |
| Necrotic Lesions | Fungal/bacterial infections |
| Wilting | Root rot, vascular pathogens |
| Pink Leaves | Genetic mutation, light exposure |
Accurately identifying these symptoms is essential for diagnosing the underlying issues and implementing appropriate interventions, ensuring the health and vibrancy of your Philodendron Brasil.
Effective Treatment Methods
To address pests and diseases affecting Philodendron Brasil Pink Leaves, it is essential to implement targeted treatment methods based on precise diagnosis and severity of the infestation or infection.
For aphid or spider mite infestations, apply a horticultural oil or insecticidal soap spray, ensuring thorough coverage of both sides of the leaves.
For fungal infections like leaf spot, utilize a fungicidal treatment containing copper or sulfur, following the manufacturer's instructions precisely.
Root rot, often caused by overwatering, necessitates repotting the plant in well-draining soil and trimming off affected roots with sterilized scissors. Regular monitoring and maintaining ideal humidity levels can prevent recurrence.
Accurate identification and prompt intervention are paramount to restoring plant health and vigor.
Soil Conditions
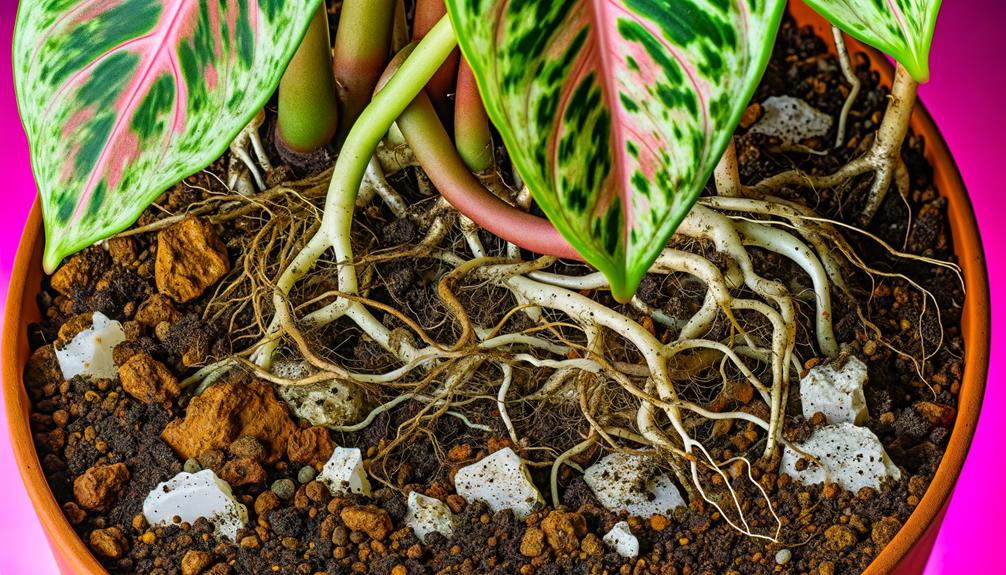

Perfect soil conditions for Philodendron Brasil Pink Leaves require a well-draining, nutrient-rich substrate that maintains sufficient moisture retention without becoming waterlogged. A mix containing equal parts of peat moss, perlite, and pine bark is recommended to ensure ideal aeration and root health.
The soil pH should be slightly acidic to neutral, ideally between 5.5 and 7.0, to facilitate nutrient uptake. Organic matter such as compost can enhance microbial activity and provide essential micronutrients. Regular soil testing is advised to monitor nutrient levels and pH balance.
Overly compacted soils or those with poor drainage can lead to root rot and other physiological stressors that may indirectly influence leaf coloration.
Stress Factors
Environmental stressors, such as irregular watering, insufficient lighting, and drastic temperature changes, can have a significant impact on the physiological health and pigmentation of Philodendron Brasil Pink Leaves.
Irregular watering disrupts the plant's water absorption, causing cellular stress and potential anthocyanin accumulation, leading to pink leaf coloration.
Insufficient lighting, especially dim light conditions, impairs photosynthesis, reducing chlorophyll production and altering pigment expression.
Drastic temperature changes, particularly sudden drops, induce oxidative stress, further affecting pigment biosynthesis.
Each of these factors can trigger a stress response, manifested as changes in leaf coloration. Understanding and mitigating these environmental stressors are crucial for maintaining the best health and aesthetic appeal of Philodendron Brasil, ensuring its characteristic variegation remains stable and vibrant.
Conclusion
To sum up, the presence of pink leaves in Philodendron Brasil can result from various factors including genetic mutations, light exposure, nutrient imbalance, watering issues, temperature fluctuations, pests, and soil conditions.
Similar to a canary in a coal mine, pink leaves serve as indicators of underlying stressors affecting plant health. Addressing these factors through scientific methods can restore the plant's typical variegation, promoting best growth and importance.
Ensuring accurate environmental conditions is crucial for maintaining the plant's physiological equilibrium.






