Tree Philodendron Care
Tree Philodendrons, indigenous to South American rainforests, require specific care. They thrive in a well-lit area, away from direct sunlight, with room temperature between 18-24°C and humidity levels of 60-70%.
The soil should be well-draining, peat-based, and the plant benefits from a balanced, slow-release fertilizer. Water when the top inch of soil is dry, using room-temperature, dechlorinated water.
Regular pruning and careful repotting help maintain health. Keep an eye out for pests like mealybugs, aphids, and spider mites.
With proper care, your Philodendron will flourish. To ensure peak growth conditions, further understanding of these plants is recommended.

Key Takeaways
- Tree Philodendrons prefer indirect sunlight and room temperatures between 18-24°C (65-75°F) with 60-70% humidity.
- Water when the top inch of soil is dry, using room-temperature, dechlorinated water to avoid overwatering and root rot.
- Use a well-draining, peat-based potting mix with a balanced, slow-release fertilizer for optimal nutrient absorption.
- Regular pruning, monitoring for pests like mealybugs, aphids, and spider mites, and repotting care are essential for overall health.
- Propagation can be achieved through cutting and ensuring proper soil conditions, including ideal pH, moisture, and nutrient levels.
Understanding Tree Philodendron Types

In the field of horticulture, understanding the diverse kinds of Tree Philodendrons is crucial for proper cultivation and maintenance. Originating from the rainforests of South America, these evergreen perennials belong to the Araceae family.
They are broadly categorized into two types: climbing and non-climbing. The climbing varieties, such as the Philodendron scandens, are characterized by their heart-shaped leaves and vine-like growth habit. Non-climbing types, such as the Philodendron selloum, exhibit bushy growth and deeply lobed, large leaves.
Each variety demands specific care conditions, including light, water, and soil requirements. Hence, as a horticulturist, it is essential to recognize these distinct types and their unique needs to promote their ideal growth and longevity.
Ideal Indoor Location
Finding the perfect spot for your Tree Philodendron within the confines of your home involves careful consideration of several factors, including light exposure, temperature, and humidity levels.
Placement near windows or glass doors is beneficial, but avoid direct sunlight which may scorch the foliage. A room temperature of around 18-24°C (65-75°F) is ideal, as temperatures below 15°C (60°F) can lead to the plant's decline.
Humidity levels should ideally remain around 60-70%. A location such as a bathroom or kitchen, where humidity tends to be higher, can be an ideal spot. However, if this is not achievable, a humidity tray or humidifier can be utilized.
Additionally, keep in mind that the Tree Philodendron requires air circulation. Avoid placing it in enclosed, stuffy areas to ensure proper growth.
Light Requirements

As we move into the discussion of light needs for Tree Philodendrons, it is crucial to highlight both the best lighting conditions and the potential dangers of overexposure.
A deep understanding of these two aspects is necessary for maintaining the health and vigor of this species.
Optimal Lighting Conditions
Balancing the right amount of light exposure is crucial for the healthy growth of a Tree Philodendron, a plant that thrives in moderate to bright, indirect sunlight. It's best positioned in a well-lit room with east or north-facing windows. This guarantees enough light penetrates the leaf surface for photosynthesis without scorching the foliage.
This plant does not tolerate direct sunlight, which can damage its leaves, reducing its ability to photosynthesize effectively. In low light conditions, this robust plant can survive, but its growth slows, and the leaf color may fade. For the best growth and health, ensure your Tree Philodendron receives ample but diffused light.
Regularly rotate your plant to make sure all sides receive adequate light, promoting symmetrical growth.
Dangers of Overexposure
While it's crucial to provide your Tree Philodendron with ample light, it's equally essential to be mindful of the potential pitfalls of overexposure.
Overexposure to direct sunlight can lead to phototoxicity, a condition where the plant's tissue is damaged, resulting in leaf burn, discoloration, and potential growth stunting. The photosynthetic process can be disrupted, causing a significant decrease in the plant's overall health and strength.
Thus, moderation and balance should be the guiding principles when considering the plant's light needs. Observe your plant's response to sunlight and adjust accordingly, ensuring it receives bright, but indirect sunlight.
Watering Techniques
Proper hydration plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and liveliness of a Tree Philodendron, which requires understanding and implementing effective watering techniques.
The techniques include:
- *Frequency*: Watering should be done when the top one inch of soil feels dry. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other diseases.
- *Volume*: Thoroughly moisten the soil, but avoid waterlogging. Ensure the pot has sufficient drainage.
- *Water Quality*: Use room-temperature, dechlorinated water to prevent shock and damage to the plant's cells.
- *Time of Day*: Watering in the morning allows the plant to effectively utilize the water throughout the day.
These techniques, when applied appropriately, can greatly improve the health and longevity of your Tree Philodendron, serving the innate purpose of nurturing life.
Soil and Fertilizer Preferences

Exploring the world of soil and fertilizer preferences, it should be emphasized that Tree Philodendrons thrive in well-draining, peat-based potting mixes and benefit greatly from the addition of a balanced, slow-release fertilizer.
The peat-based mix provides an ideal environment for root growth, while ensuring adequate water retention and air circulation. The soil pH should ideally be between 6.0 and 7.0, a slightly acidic to neutral range, to promote nutrient absorption.
A slow-release fertilizer, preferably with a 20-20-20 NPK ratio (Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Potassium), should be applied every two to three months during the growing season. This provides a steady supply of essential nutrients, enhancing the plant's overall health and appearance.
Pruning and Repotting Guide
The care of Tree Philodendron involves understanding its soil and fertilizer preferences. It also involves mastering the art of pruning and repotting.
Our focus now shifts to these essential maintenance practices. We will start with the basics of pruning and then move on to repotting essentials. We will also cover the critical steps to maximize post-repotting care.
These procedures, when executed correctly, can greatly enhance the health, growth, and longevity of your Tree Philodendron.
Pruning Basics
One must understand that successful pruning of a tree philodendron involves careful timing, the correct tools, and a thorough understanding of the plant's growth patterns. It's an exercise in precision and patience, serving not just the plant, but also the environment in which it thrives.
- Timing: The best time to prune is during the growing season, typically in the spring or early summer.
- Tools: Use sharp, clean pruning shears to minimize damage and prevent the spread of disease.
- Growth Patterns: Recognize the signs of new growth, such as leaf buds, to avoid cutting off potential new stems.
- Safety: Always wear gloves and safety glasses when pruning to protect yourself from the plant's toxic sap.
Repotting Essentials
Understanding the nuances of repotting a tree philodendron is just as crucial as mastering the art of pruning, as it necessitates precise knowledge of the plant's root structure, ideal soil composition, and the appropriate pot size. The roots should be meticulously examined for any signs of disease or pests before repotting. A high-quality, well-draining potting mix is recommended; it should be rich in organic matter and have a slightly acidic pH.
| Factors | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Pot Size | Should accommodate the root system with space for growth. Avoid excessively large pots as they can result in waterlogging. |
| Soil Composition | A well-draining, peat-based mixture. Include perlite for additional drainage. |
| Root Inspection | Inspect for pests, diseases. Trim any deceased, mushy roots. |
This meticulous process safeguards the health and vitality of your tree philodendron, enabling it to continue fulfilling its purpose in enhancing your surroundings.
Post-Repotting Care
Moving through post-repotting care procedures, which involve careful watering, regular monitoring, and timely pruning, is essential to ensure your tree philodendron thrives in its new environment. Here are some key steps to take into account for successful post-repotting care:
- Watering: Avoid waterlogging the soil. Instead, aim for consistent moisture. Overwatering can lead to root rot, a common post-repotting issue.
- Monitoring: Regularly check the plant for signs of stress, like yellowing leaves or wilting. Early detection can help you take corrective actions promptly.
- Pruning: Trim off any dead or dying leaves to redirect the plant's energy towards new growth.
- Feeding: After repotting, wait for about 4-6 weeks before you begin fertilizing. This allows the plant to adjust to its new environment.
With these steps, your tree philodendron should thrive post-repotting.
Common Pests and Diseases
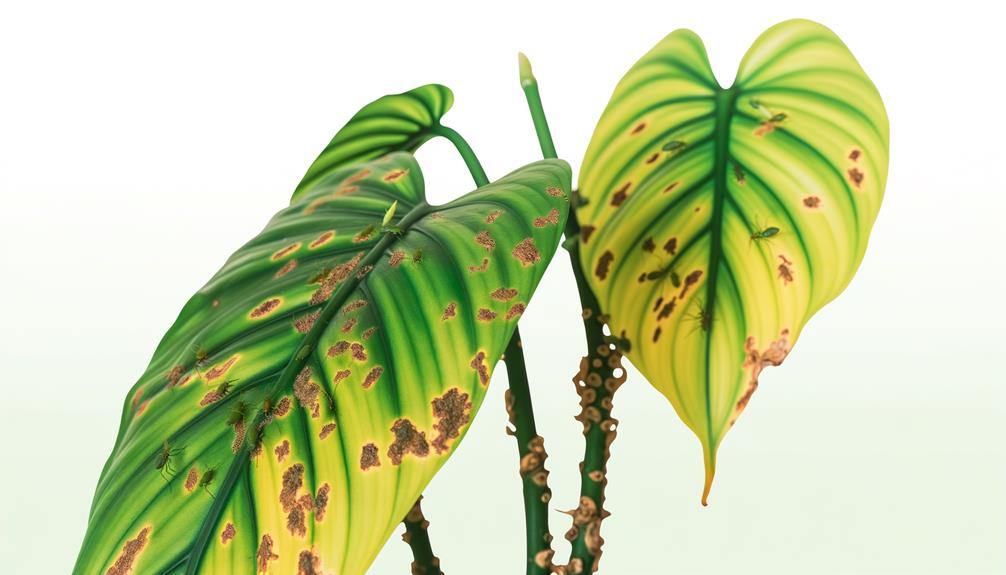

While tree philodendrons are generally resistant to many diseases, they can be vulnerable to several types of pests. Mealybugs, aphids, and spider mites are common culprits, causing significant harm if not promptly addressed. Mealybugs appear as fluffy white masses and drain the plant's nutrients, leading to yellowing and wilting leaves.
Aphids, small pear-shaped insects, excrete a sticky substance called honeydew that promotes mold growth. Spider mites, almost invisible to the naked eye, cause stippled or yellowing leaves, often with fine webbing. Management strategies include regular inspection, maintaining ideal plant health, and biological control methods such as introducing beneficial insects.
In severe infestations, specific insecticides may be necessary. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) practices are recommended for sustainable control.
Propagation Methods
Propagation of the Tree Philodendron, a tropical genus native to rainforests, can be achieved effectively through two primary methods: the cutting propagation process and soil preparation.
The cutting propagation process is a vegetative method that involves the separation and rooting of a portion of the parent plant.
Soil preparation, on the other hand, entails the creation of ideal conditions including proper pH balance, moisture levels, and nutrient content to foster successful growth and development of the propagated plant.
Cutting Propagation Process
Employing the cutting propagation method, one can effectively multiply their Tree Philodendron. This process involves careful selection, cutting, and cultivation of the plant's stems or leaves.
This method is particularly advantageous for its speed and efficiency, and comprises several key steps:
- Selection: Choose a healthy, mature leaf or stem from an existing plant. This forms the basis of the new plant.
- Cutting: Make a clean cut below a node or leaf joint, ensuring it includes an 'eye' or growth point.
- Rooting: Place the cutting in a container with water or moist potting mix. This stimulates root growth.
- Cultivation: Once roots have formed, transplant the cutting into a pot with suitable growing conditions for a Tree Philodendron.
Adopting these practices can help others experience the joy of growing their own Tree Philodendrons.
Soil Preparation Tips
In the domain of propagation methods, careful preparation of the soil is an essential step, designed to guarantee the best suitable environment for the new Tree Philodendron cuttings to thrive.
A rich, well-draining soil, preferably comprised of a balanced mix of peat, perlite, and organic compost, is ideal. The pH level should be slightly acidic, between 6.0 and 7.0.
Soil preparation begins with sterilization, which prevents the introduction of harmful pathogens into the cutting's environment. This can be achieved by baking the soil mix at 180°F for 30 minutes.
Once cooled, the soil should be moistened but not waterlogged, providing the most favorable conditions for root development. Remember, successful cultivation lies in meticulous preparation.
Temperature and Humidity Needs
When cultivating Tree Philodendron, understanding its specific temperature and humidity requirements is essential for best growth and health. This tropical plant thrives in a warm, humid environment, emulating its natural habitat.
- The ideal temperature range for Tree Philodendron is between 65°F and 85°F. Temperatures below 55°F can harm the plant.
- The humidity level should ideally be above 60%. Using a humidifier or placing the plant on a water-filled tray with pebbles can help maintain this.
- The plant is sensitive to sudden temperature changes, so avoid placing it near heating or cooling vents.
- Similarly, avoid exposing it to direct drafts from doors and windows, which can cause leaf damage.
Growth Expectations
Understanding the growth expectations of the Tree Philodendron is important for anticipating its care needs and ensuring its most favorable development.
This evergreen perennial typically grows up to 15 feet in its natural habitat, but when domestically cultivated, it's usually confined to about 6 feet. Growth rates are influenced by several factors such as light levels, temperature, and the quality of care provided.
Under ideal conditions, this species may grow up to 2 feet annually. New foliage emerges from the tips of elongated stems giving it a tree-like appearance. The leaves are large, often 12 to 18 inches long, and deeply lobed.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
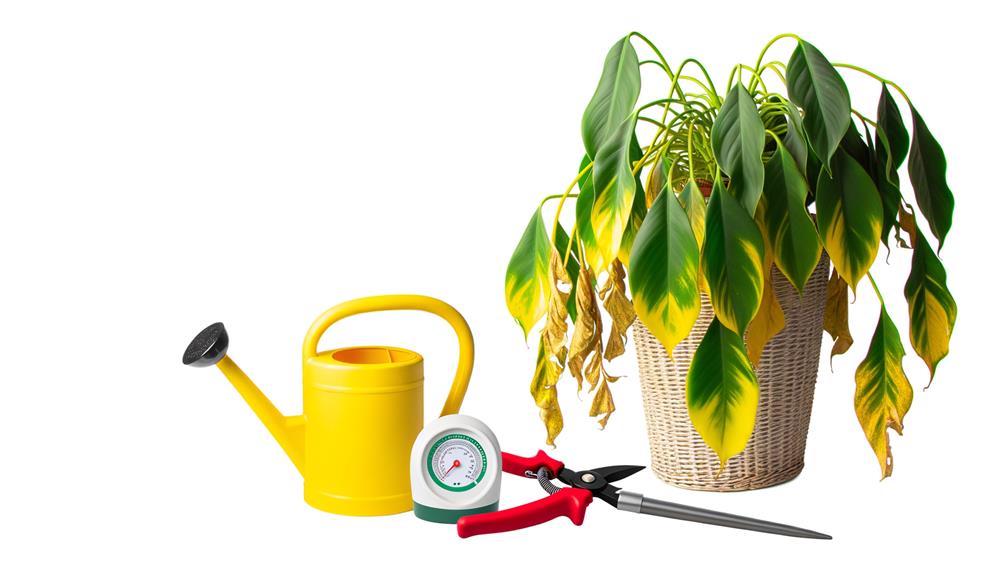

Despite its sturdy nature, the Tree Philodendron can encounter a variety of common problems that may impede its growth and overall health, requiring attentive care and a keen understanding of plant pathology.
Recognizing and addressing these issues promptly can make a significant difference in the plant's well-being.
These challenges include:
- Overwatering: This can lead to root rot, a serious condition that can be fatal if not addressed quickly.
- Underwatering: Conversely, insufficient watering can result in wilting or yellowing leaves.
- Inadequate Light: Tree Philodendron thrives in bright, indirect light. Lack of sufficient sunlight can stunt growth and cause leaf drop.
- Pest Infestations: Aphids, mealybugs, and spider mites can all pose a significant threat to the plant's health.
Each of these problems requires a unique solution, tailored to promote optimal plant health.
Conclusion
To sum up, tree philodendrons are akin to the virtuosos of the plant realm, flourishing under specific conditions. Proper comprehension of their light, water, and soil preferences, along with accurate temperature and humidity management, can lead to a flourishing plant.
Through appropriate propagation techniques, these lush companions can multiply, enhancing the natural aesthetics of indoor spaces. Addressing common problems promptly promotes their vibrant growth, making tree philodendron care a rewarding pursuit.






